Find keyword or terms by letter
Click on a numbered or lettered box below to show list of keywords and terms.
Cabinet Secretary

(Context: General)
Definition
An officer of the Governor's Cabinet appointed to oversee the operations of a group of functionally related agencies.
Cable Modem
(Context: )
Definition
A cable modem provides variable speed transmission depending on the number of simultaneous users on the same cable
Calendar Unit
(Context: Project Management)
Definition
1. The smallest unit of time used in scheduling the project. Calendar units are generally in hours, days, or weeks, but can also be in quarter years, months, shifts, are even in minutes.
2. Calendar units are essential to the proper management of a project. They are the time measurements that are used to plan the entirety of a projects schedule events in a logical manner. Calendar units will typically refer to the smallest possible measurement of time that can be appropriately used in reference to a particular project or a particular activity scheduled within the project as a whole. Possible calendar units are all standard time measurements, such as minutes, hours, days, weeks, months, and, in some long term projects, years.
1. PMBOK
2. Calendar Unit - Project Management Knowledge (project-management-knowledge.com)
Capital Asset
(Context: General)
Definition
Tangible property, including durable goods, equipment, buildings, installations, and land.
CCA
Cascading Style Sheets (CSS)

(Context: Software)
Definition
An XML protocol used to control formatting of Web pages.
Cascading Style Sheets (w3.org)

Category Cat 5 / Cat 5e / Cat 6 / Cat 6a / Cat 7 / Cat 7a / Cat 8.1 / Cat 8.2

(Context: Hardware)
Definition
A standard twisted pair cable for computer networks.
Cat5e provides performance of up to 100 MHz and is suitable for most varieties of Ethernet over twisted pair up to 1000BASE-T (Gigabit Ethernet). It is also used to carry other signals such as telephony and video.
Standard types of twisted pair cabling Name Typical construction Bandwidth Applications Notes Level 1 400 kHz Telephone and modem lines Not described in EIA/TIA recommendations. Unsuitable for modern systems.[17] Level 2 4 MHz Older terminal systems, e.g. IBM 3270 Not described in EIA/TIA recommendations. Unsuitable for modern systems.[17] Cat 3 UTP[18] 16 MHz[18] 10BASE-T, 100BASE-T4[18] Described in EIA/TIA-568. Unsuitable for speeds above 16 Mbit/s. Now mainly for telephone cables.[18] Cat 4 UTP[18] 20 MHz[18] 16 Mbit/s Token Ring[18] Not commonly used[18] Cat 5 UTP[18] 100 MHz[18] 100BASE-TX, 1000BASE-T[18] Common for current LANs. Superseded by Cat 5e, but most Cat 5 cables meet Cat 5e standards.[18] Limited to 100 m between equipment. Cat 5e UTP,[18] F/UTP, U/FTP[19] 100 MHz[18] 1000BASE-T, 2.5GBASE-T[18] Enhanced Cat 5. Common for current LANs. Same construction as Cat 5, but with better testing standards.[18] Limited to 100m between equipment. Cat 6 UTP,[18] F/UTP, U/FTP[20] 250 MHz[18] 5GBASE-T, 10GBASE-T ISO/IEC 11801 2nd Ed. (2002), ANSI/TIA 568-B.2-1. Limited to 55 m distance at 10GBASE-T Cat 6A UTP, F/UTP, U/FTP, S/FTP 500 MHz 5GBASE-T, 10GBASE-T Improved standards, tested to 500 MHz. Full 100 m distance at 10GBASE-T ISO/IEC 11801 2nd Ed. Am. 2. (2008), ANSI/TIA-568-C.1 (2009) Cat 7 S/FTP, F/FTP 600 MHz[21] ? ISO/IEC 11801 2nd Ed. (2002). Only with GG45 or TERA connectors. It is not recognized by the EIA/TIA. Cat 7A S/FTP, F/FTP 1 GHz[21] ? ISO/IEC 11801 2nd Ed. Am. 2. (2008). Only with GG45 or TERA connectors. It is not recognized by the EIA/TIA. Cat 8.1 F/UTP, U/FTP 2 GHz[21] 25GBASE-T, 40GBASE-T ANSI/TIA-568-C.2-1, ISO/IEC 11801-1:2017 Cat 8.2 S/FTP, F/FTP 2 GHz 25GBASE-T, 40GBASE-T ISO/IEC 11801-1:2017 
CDMA 2000

(Context: General)
Definition
1. Code division multiple access (CDMA) version of the IMT-2000 standard developed by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU). The CDMA2000 is third generation (3-G) mobile wireless technology that can provide mobile data communications at speeds ranging from 144 Kbps to 2 Mbps. Deployment is in the planning stages.
2. The cdma2000 system is an evolutionary enhancement of the IS-95 standards which support 3G services defined by the International Telecommunications Union (ITU). cdma2000 comes in two phases: 1XRTT and 3XRTT (1X and 3X indicates the number of 1.25 MHz wide radio carrier channels used and RTT stands for Radio Transmission Technology). The cdma2000 1XRTT, which operates within a 1.25 MHz bandwidth, can be utilized in existing IS-95 CDMA channels as it uses the same bandwidth, while 3XRTT requires the commitment of 5 MHz bandwidth to support higher data rates.
2. NIST Journal of Research Abstract
Library of Congress CDMA2000 Evolution: System concepts and design principles
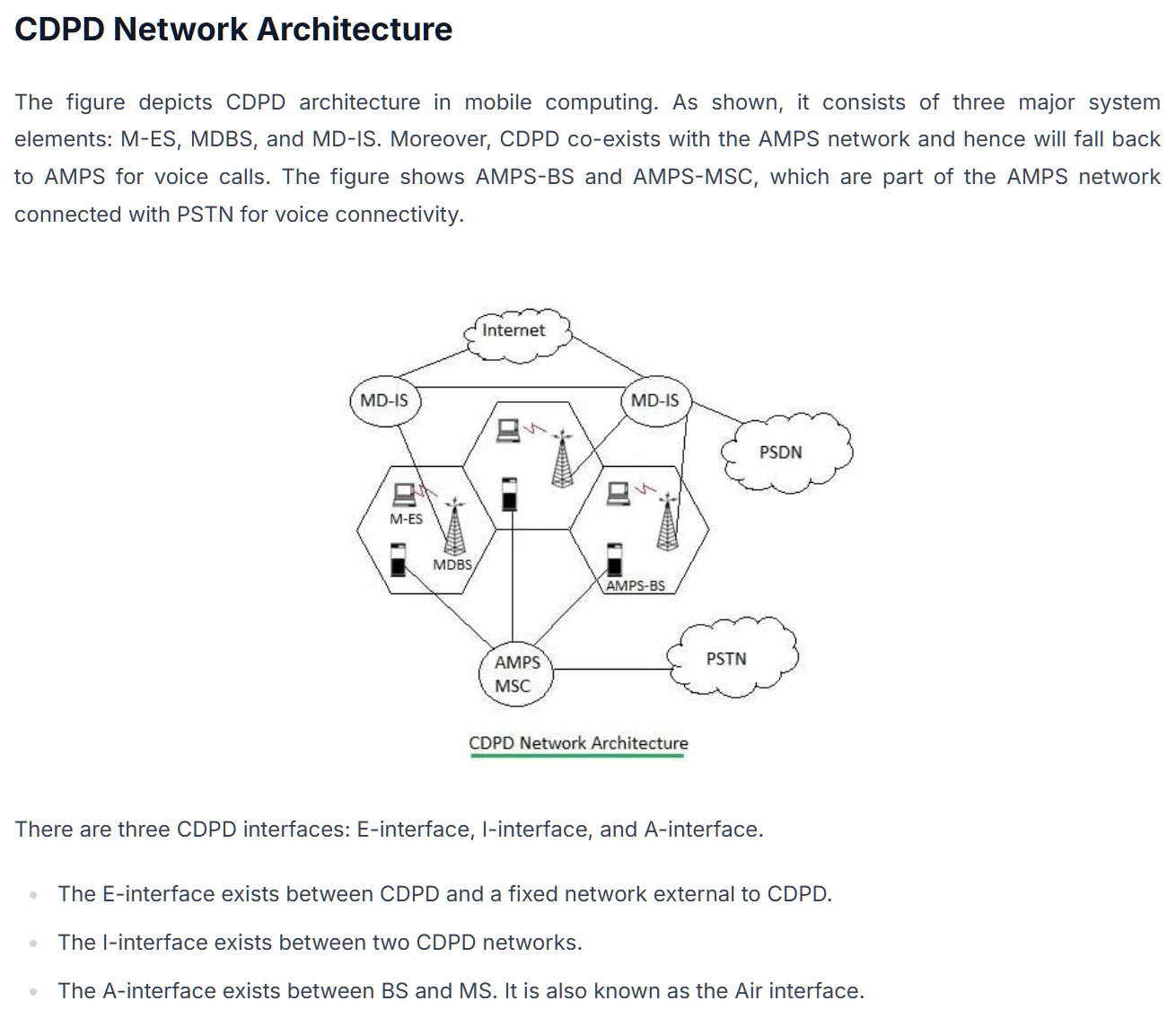
Cellular Digital Packet Data (CDPD)

(Context: General)
Definition
Cellular Digital Packet Data, or as it’s more commonly called, CDPD, consists of using cellular radio repeaters for the transmission of small bursts of data known as packets. The CDPD process allows the insertion of packets of data in between lightly modulated cellular radio voice channels without reducing cell phone voice capabilities. CDPD is an open transmission methodology for sending data on existing Advanced Mobile Phone Service (AMPS) cellular networks at a transmission rate of 19.2 kilobits per second. The network architecture uses the protocol used in the Internet (i.e., Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol, or TCP/IP).
CDPD utilizes existing cellular telephone network to transmit data. It uses an idle channel in existing analog cellular systems to provide a connectionless service. When a channel is not being used for voice traffice, it can be used to send and receive packets from the CDPD-equipped mobile station. Cellular channel can be shared between voice and data service in this way, or the cellular carrier can remove some channels from voice service and dedicate them exclusively to data service. CDPD is best-suited for the shot and bursty data transmissions such as messaging, despatch, packet tracking, and remote device monitoring. https://www.andrew.cmu.edu/user/rk2x/telclass.dir/oldstudentprojects.dir/proj3.dir/cdpd.html
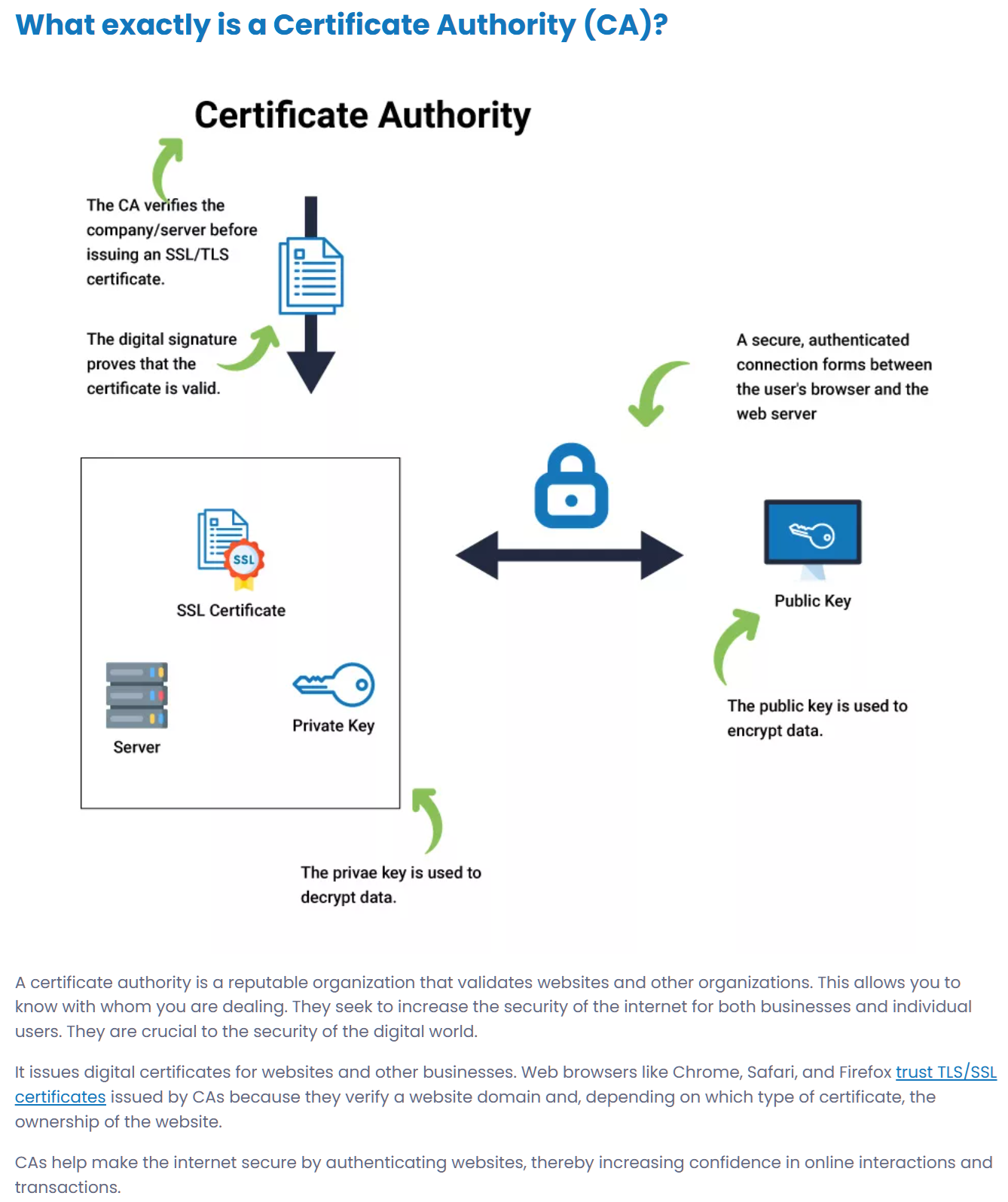
Certificate authority (CA)

(Context: Information Systems Security)
Definition
1. A system for managing certified digital signatures. Manages the implementation of policies to authenticate, authorize and revoke the assignment of keys to users.
2. A trusted entity that issues and revokes public key certificates.
Sources:
NIST SP 1800-16B under Certificate Authority from NISTIR 8149
NIST SP 1800-16C from NISTIR 8149
NIST SP 1800-16D under Certificate Authority from NISTIR 8149
NIST SP 1800-21C
NISTIR 8149Change Control
(Context: Information Systems Security, Technology Management)
Definition
(Context: Information Systems Security)
1. A management process to provide control and traceability for all changes made to an application system or information system.
(Context: Technology Management)2. Identifying, documenting, approving or rejecting, and controlling changes to the project baselines.
2. Project Management Institute (PMI) Terms (certificationacademy.com)
Change Control Board (CCB)
(Context: Project Management)
Definition
A formally constituted group of stakeholders responsible for reviewing, evaluating, approving, delaying, or rejecting changes to the project, with all decisions and recommendations being recorded.
Project Management Institute (PMI) Terms (certificationacademy.com)
Change Management Process
(Context: Project Management)
Definition
A set of tasks or procedures established to ensure that project performance is measured to the baseline and changes are reviewed, approved, or rejected and the baseline updated.
Chart of Accounts
(Context: Project Management)
Definition
Any numbering system used to monitor project costs by category (e.g., labor, supplies, and materials). The project chart of accounts is usually based upon corporate chart of accounts of the primary performing organization.

Chief Information Officer of the Commonwealth (CIO)

(Context: Technology Management)
Definition
Oversees the operation of the Virginia Information Technologies Agency (VITA) and exercises the powers and performs the duties conferred or imposed upon him by law and performs such other duties as may be required.
Code of Virginia Code - Chapter 20.1. Virginia Information Technologies Agency
Chief Information Security Officer of the Commonwealth (CISO)

(Context: Technology Management)
Definition
The senior management official designated by the CIO of the Commonwealth to develop Information Security policies, procedures, and standards to protect the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information systems and data.
https://www.cisa.gov/sites/default/files/publications/Virginia_Cyber_Governance_Case_Study_2.pdf
Government Technology Magazine May/June 2024 (flippingbook.com)
Code of Virginia Code - Chapter 20.1. Virginia Information Technologies Agency
Citizen Facing Website
(Context: General, Enterprise Architecture)
Definition
Any public, indexable website deployed on behalf of the Commonwealth.

Clickwrap

(Context: Technology Management)
Definition
A clickwrap or clickthrough agreement is a prompt that offers individuals the opportunity to accept or decline a digitally mediated policy. Privacy policies, terms of service and other user policies, as well as copyright policies commonly employ the clickwrap prompt.
EA-Solution-Computer-based-Signature-Standard.pdf (virginia.gov)
A Comprehensive Guide to the Law of Online Contracts - McCarthy Law Group
Cloud Aware
(Context: Hosting Options, Software)
Definition
An application designed to utilize one or more Cloud services to support the Capabilities and Features that the application provides.
Cloud Aware vs Cloud Native: 7 Differences You Need to Know (castordoc.com)
What Makes an App Cloud-Aware? (06:09) Business will reduce computing cost, allow more focus on important work, and increase agility. Cloud-Aware applications are location independent and discoverable; Films Media Group - Cloud-Aware Applications: An Introduction
Cloud Computing
(Context: Hosting Options, Software)
Definition
Is a model for enabling ubiquitous, convenient, on-demand network access to a shared pool of configurable computing resources (e.g., networks, servers, storage, applications, and services) that can be rapidly provisioned and released with minimal management effort or service provider interaction.
Cloud readiness / Cloud-ready
(Context: Hosting Options, Software, Virtual Server)
Definition
Cloud Readiness / Cloud ready - Cloud readiness is defined as an IT solution that is either already hosted or can be hosted on a virtual server using either Linux or Windows as an operating system and there are no software licensing or data issues with the solution consuming cloud-based hosting services. There are nine possible migration paths for each agency/customer IT solution that is not already hosted by cloud-based services.
Preferred – IT solution is hosted on a virtual x86 or equivalent server using either Linux or Windows as an operating system. This also includes any IT solution under ECOS evaluation.
Acceptable – IT solution is hosted on a non Windows/Linux virtual machine (examples: AIX, Solaris) that could be hosted by either a private cloud or by a community/public cloud provider licensing or data issues with the solution consuming cloud-based hosting services.
Cloud_Based_Hosting_Topic_Report_FINAL.pdf | https://www.vita.virginia.gov/media/vitavirginiagov/it-governance/psgs/pdf/Cloud_Based_Hosting_Topic_Report_FINAL.pdf
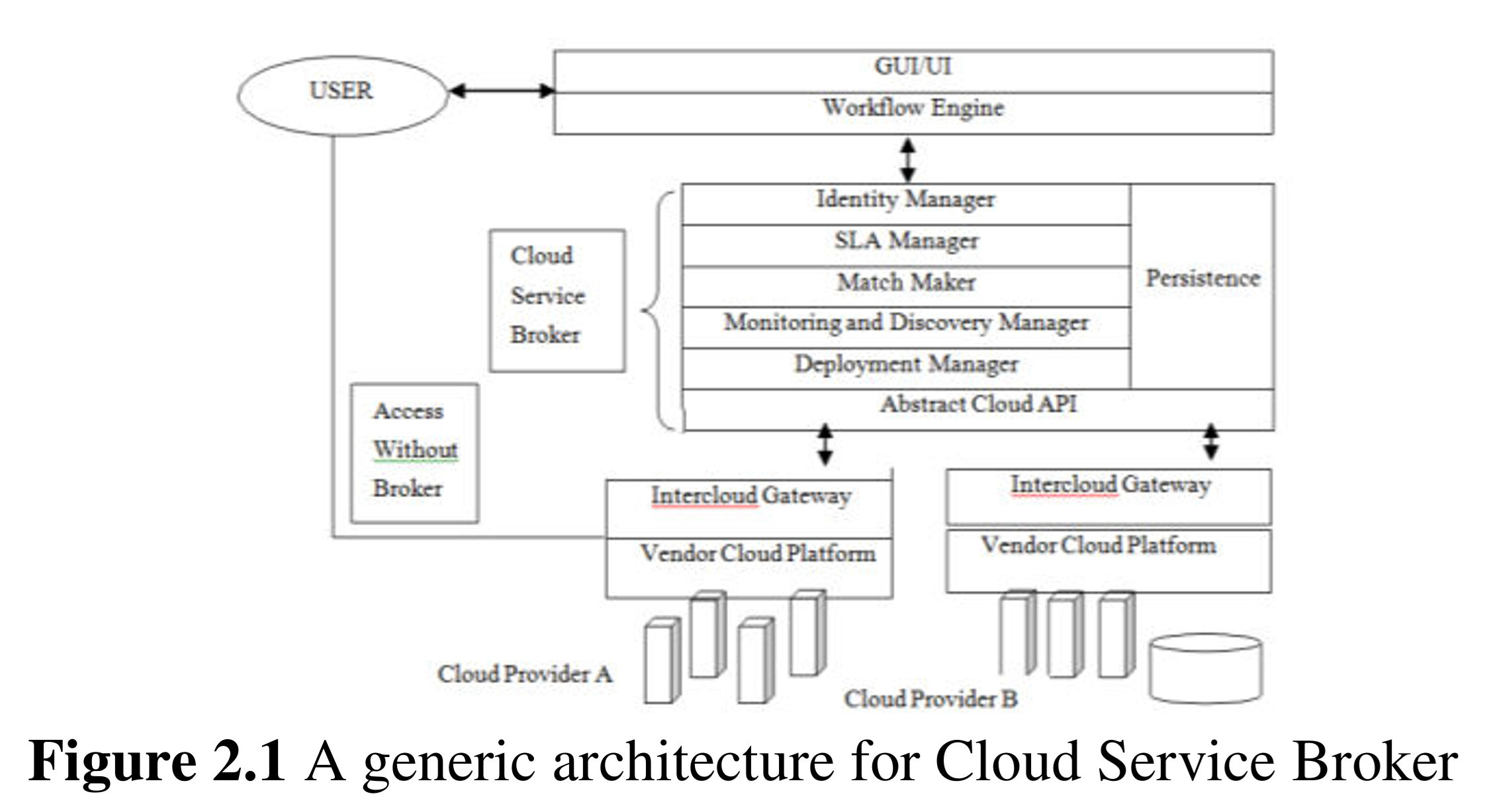
Cloud Service Broker (CSB)

(Context: Hosting Options, Software)
Definition
An entity (real or virtual) that manages the use, performance and delivery of cloud services, in addition to enabling the negotiations and relationships between cloud providers and cloud consumers. NIST defines CSB as an IT role and business model in which a company or other entity adds value to one or more (public or private) cloud services on behalf of one or more consumers of that service via three primary roles including aggregation, integration and customization brokerage.
Cloud_Based_Hosting_Topic_Report_FINAL.pdf | https://www.vita.virginia.gov/media/vitavirginiagov/it-governance/psgs/pdf/Cloud_Based_Hosting_Topic_Report_FINAL.pdf
Cloud Service Integrator (CSI)
(Context: Hosting Options)
Definition
Specializes in the integration of cloud hosted services (sometimes referred to as Integration-as-a-Service). For the extended hybrid cloud model some of the IT solutions, services and data are maintained locally, while others are served remotely via multiple cloud providers.
Co-Location / Colocation (COLO)
(Context: Data Center Facility, Project Management)
Definition
(Context: Project Planning)
An organizational placement strategy where the project team members are physically located close to one another in order to improve communication, working relationships, and productivity.
(Context: Operations)
A data center facility in which a business can rent space for servers and other computing hardware. Typically, a COLO provides the building, cooling, power, bandwidth and physical security while the customer provides servers and storage.
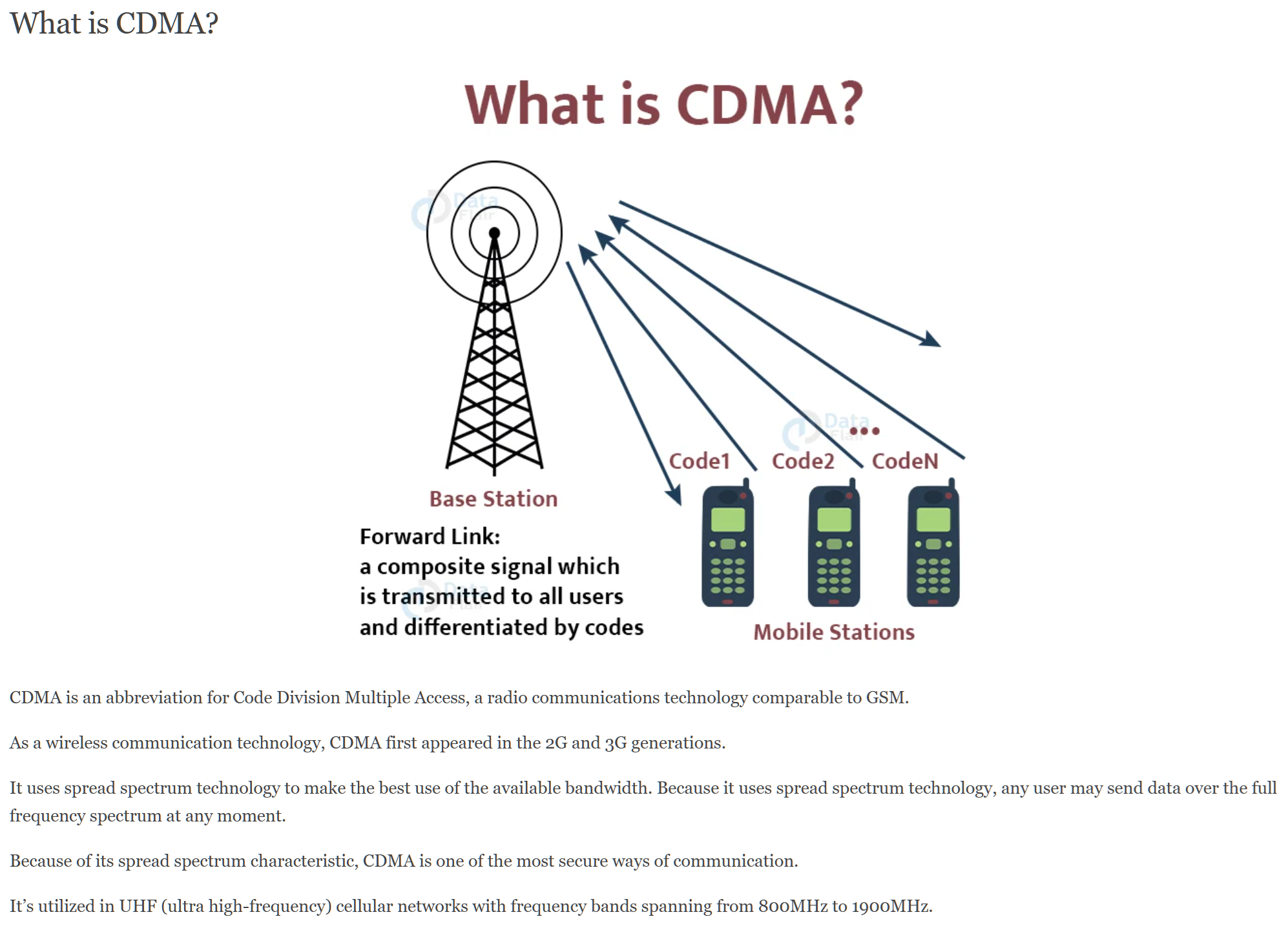
Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA)

(Context: General)
Definition
A form of multiplexing where the transmitter encodes the signal using a pseudo-random sequence which the receiver also knows and can use to decode the received signal. Each different random sequence corresponds to a different communication channel. Motorola uses CDMA for digital cellular phones. Qualcomm pioneered the introduction of CDMA into wireless telephone services.
Understanding the Differences: CMDA vs TDMA in Cellphone Architectures
Code of Accounts
(Context: Project Management)
Definition
Any numbering system used to uniquely identify each component of the work breakdown structure.
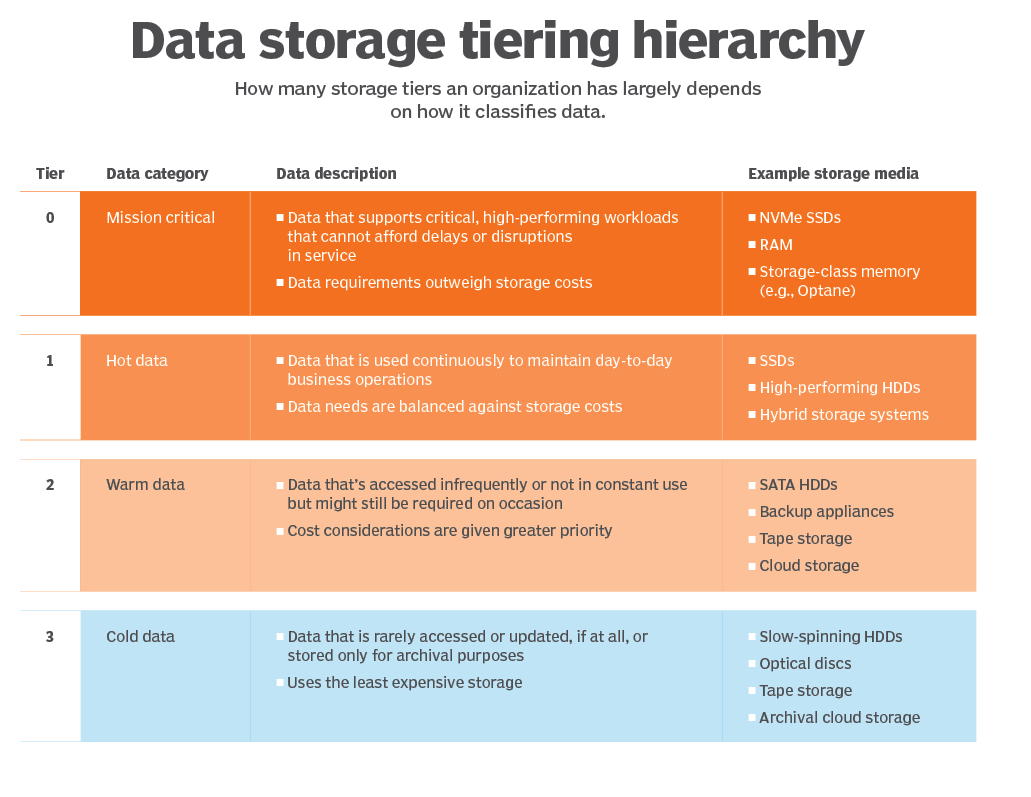
Cold Data Storage

(Context: Data Center Facility, Hardware, Technology Management)
Definition
Refers to the storage of data in a manner that minimizes costs while still allowing some level of access and use.
https://www.vita.virginia.gov/media/vitavirginiagov/it-governance/ea/pdf/Event-Log-Management.pdf
Collaboration Opportunity
(Context: General, Technology Management)
Definition
A common business need that establishes the opportunity for organizations and/or political subdivisions to work together, in a substantive, mutually beneficial relationship, towards a common integrated solution. In preparation for the annual RTIP Report, agency IT investments are evaluated as potential Collaboration Opportunities.
Technology Business Strategies - Commonwealth Technology Business Plan
Commercial off-the-shelf (COTS)
(Context: Hardware, Software)
Definition
A term for software or hardware products that are ready-made and available for sale to the general public. They are often used as alternatives to in-house developments or one-off government-funded developments (GOTS). The use of COTS is being mandated across many governments and business programs, as they may offer significant savings in procurement and maintenance. Commercial off-the-shelf.

Common Internet File System (CIFS)

(Context: Software)
Definition
Specifies the Common Internet File System (CIFS) Protocol, a cross-platform, transport-independent protocol that provides a mechanism for client systems to use file and print services made available by server systems over a network.
CIFS is a remote file system access protocol that allows groups of users to work together and share documents via the internet or their corporate intranets. CIFS is an open, cross-platform technology based on the native file-sharing protocols built into Microsoft Windows and other operating systems. It is supported on numerous platforms, including Unix.
Commonwealth Asset Management
(Context: Technology Management)
Definition
The process of planning, procuring, deploying, operating, maintaining, upgrading, and disposing of assets to achieve maximum return on investment over the lifecycle of the asset, in support of both Commonwealth and agency IT strategic plans.
Commonwealth Data
(Context: Commonwealth Data Management Program, Technology Management)
Definition
Data maintained, transformed or stored by an agency or it's designee in the performance of Commonwealth business.
Commonwealth of Virginia (COV)
(Context: General)
Definition
The government of the Commonwealth of Virginia, and its agencies.
"Agency" means any department, institution, authority, instrumentality, board or other administrative agency of the government of the Commonwealth of Virginia"
https://www.vita.virginia.gov/policy--governance/governance/cov-it-glossary/
Commonwealth of Virginia Computer Incident Response Team (COV CIRT)
(Context: Information Systems Security)
Definition
A function of the Incident Management division of the COV Security Services Directorate. The COV CIRT operates under the direction of the Incident Management Director and is primarily comprised of the Incident Management engineers, with additional resources to be drawn as needed on a per-incident basis from IT Partnership technical, legal and human resources staff.
Commonwealth Project (CP)
(Context: Project Management)
Definition
A temporary endeavor, undertaken by a Commonwealth executive branch agency (or agencies), to deliver a unique product or service. Commonwealth projects are expected to follow project management best practices and comply with project management requirements identified in the Code of Virginia, Governor's Executive Orders, and COV ITRM policies, standards, and guidelines.
Commonwealth Project Management (CPM)
(Context: Project Management)
Definition
The application of knowledge, skills, tools, and techniques to meet or exceed stakeholder needs and expectations from a Commonwealth Project.
Commonwealth Technology Management (CTM)
(Context: Technology Management)
Definition
In the Commonwealth of Virginia, it is the application of information technology investment management (ITIM) principles and practices in support of the business activities of state government.
Communications Services
(Context: Technology Management)
Definition
Service that includes telecommunications services, automated data processing services and management information systems that serve the needs of state agencies and institutions. (§2.2-2001 of the Code of Virginia)
Community Cloud
(Context: Hosting Options, Technology Management)
Definition
The cloud infrastructure is provisioned for exclusive use by a specific community of consumers from organizations that have shared concerns (e.g., mission, security requirements, policy, and compliance considerations). It may be owned, managed, and operated by one or more of the organizations in the community, a third party, or some combination of them, and it may exist on or off-premises.
Cloud_Based_Hosting_Topic_Report_FINAL
Complex Event
(Context: General, Technology Management)
Definition
An that has caused a complete and immediate work stoppage across the Enterprise, affecting multiple agencies across multiple lines of business. The expectation is that the service will not be fully reestablished within the SLAs for and/or .
Examples: total or failure that impacts a significant portion of the SAN, WAN, or private cloud.
Complexity
(Context: Project Management)
Definition
The technological and management characteristics of a project and the potential impacts, both positive and negative, that these characteristics could have on the project risks. Complexity is a Risk modifier in that it can exacerbate or mitigate the impact of Risk on the successful completion of the project.
Component
(Context: Software)
Definition
A readily accessible and observable aspect of a technology topic, such as Test Management is a component of the Software Engineering topic in the Application Domain. A component is not the individual pieces such as tables, SQL scripts, etc. and other many similar pieces which make up the component.
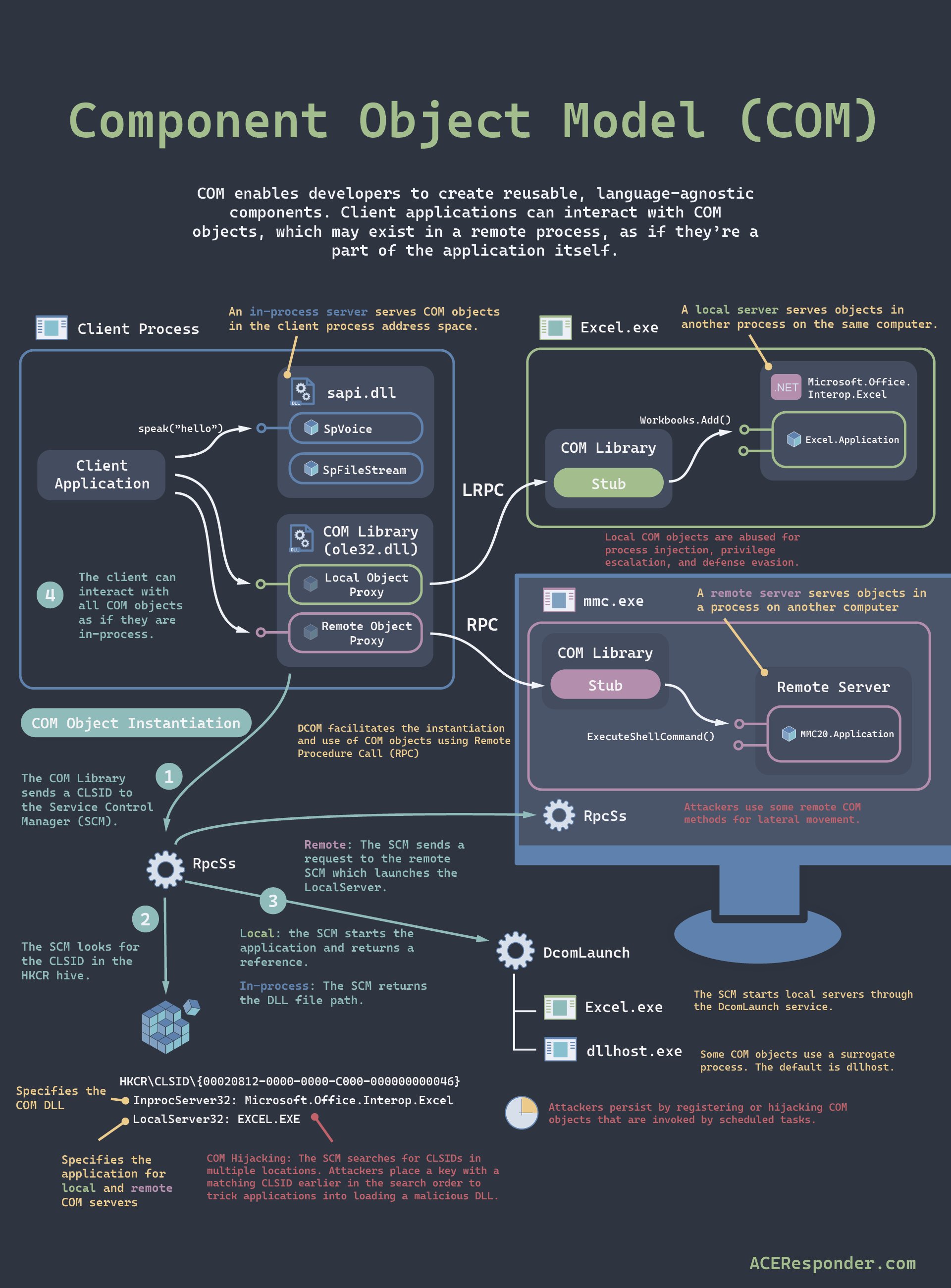
Component Object Model (COM)

(Context: Software)
Definition
Component Object Model (Microsoft); also DCOM and DCOM+ for distributed systems
Over the years, COM has provided the foundation for numerous Microsoft products and technologies.
COM defines a binary interoperability standard for creating reusable software components that can interact with each other at runtime. This includes a standard protocol and wire format that COM objects use to interact when running on different hardware components.
COM standardizes function calls between components and provides a base interface for component interaction without requiring an intermediary system component.
Computer Database
(Context: General, Software)
Definition
A structured collection of data or records residing in a computer.
Computing Devices
(Context: Hardware)
Definition
A computing device is a hardware component or system of components that allow a user to interact with a computer, a telephone system, or other electronic information system.
Conceptual Project Planning
(Context: Project Management)
Definition
The process of developing broad-scope project documentation from which the technical requirements, estimates, schedules, control procedures, and effective project management will all flow.
Condition
(Context: General, Software)
Definition
Risk Statement: In a risk statement, the condition phrase is the phrase at the beginning of the statement. (SEI)
General: The principal circumstances, situations, etc., that are causing concern, doubt, anxiety, or uncertainty.
Phrase: A condition phrase is a phrase that describes a situation or circumstance that must be met before something else can happen.
How to write a good risk statement - DAU
COV ITRM Glossary › R › Risk Statement (also known as Statement of Risk) | Virginia IT Agency
Confidentiality
(Context: Security)
Definition
The protection of data from unauthorized disclosure to individuals or information systems.
DATA CONFIDENTIALITY: IDENTIFYING AND PROTECTING ASSETS AND DATA AGAINST DATA BREACHES - NIS NCCOE
Config
(Context: Software)
Definition
A configuration file used by various applications. It contains plain-text parameters that define settings or preferences for building or running a program.
https://www.vita.virginia.gov/media/vitavirginiagov/it-governance/ea/pdf/Event-Log-Management.pdf
Configuration Management
(Context: Project Management, Security)
Definition
A technical and management process for establishing and maintaining consistency of a product's functional and physical attributes with its requirements, design, and operational information throughout its life. The major CM functions are Management and Planning; Configuration Identification; Configuration Change Management; Configuration Status Accounting; and Configuration Verification and Audit. (Context: Project Management)
A formal discipline that provides project team members and customers with the methods and tools that are used to identify the product developed, establish baselines, control changes to these baselines, record and track status, and audit the product. (Context: Information Systems Security)
MIL-HDBK 61A, ANSI/EIA 649-B-2011
Configuration Management System
(Context: Project Management, Technology Management)
Definition
A subsystem of the overall project management system. It is a collection of formal documented procedures used to apply technical and administrative direction and surveillance to: identify and document the functional and physical characteristics; record and report each change and its implementation status; and support the audit of the products, results or components to verify conformance to requirements. It includes the documentation, tracking systems and defined approved levels necessary for authorizing and controlling changes. In most application areas, the configuration management system includes the change control system.
Consequence
(Context: Software)
Definition
A single phrase or sentence that describes the key, possible negative outcome of the current conditions.
Background: Capturing a statement of risk involves considering and recording the conditions that are causing concern for a potential loss to the project, followed (optionally) by a brief description of the potential consequences of these conditions.
Continuous Risk Management Guidebook - SEI Carnegie Mellon University p41 of 562
Constraint
(Context: Project Management)
Definition
The state, quality, or sense of being restricted to a given course of action or inaction. An applicable restriction or limitation, either internal or external to the project that will affect the performance of the project or a process.
Container
(Context: Hosting Options, Virtual Server)
Definition
A packaging format that encapsulates a set of software with its dependencies and runs in a virtual server environment with a minimal OS. Therefore, it is a form of virtualization. The difference between VM's and containers is that each VM has its own full sized OS, while containers have a minimal OS.
Container Orchestration
(Context: Hosting Options, Software, Virtual Server)
Definition
Container Orchestration: Container orchestration is the automated process of managing and coordinating the deployment, scaling, and networking of containerized applications, simplifying the complex tasks associated with managing large numbers of containers. Container orchestration systems automate the deployment and scaling activities of the container runtime engines.
Container Runtime
(Context: Software, Virtual Server)
Definition
Container runtime: A platform that allows you to instantiate container images as an executable process, providing the bridging between the container’s internal resources and the host kernel. Often container runtimes provide a control plane to provide the necessary rules and controls to handle scale out events, resource access and limits. The container runtime often works together with a container orchestration system.
Containerization
(Context: Hosting Options, Virtual Server)
Definition
Containerization is a software deployment process that bundles an application’s code with all the files and libraries it needs to run on any infrastructure. It is therefore the encapsulation of an application in a container.
Contingency Planning
(Context: Technology Management)
Definition
The development of a management plan that identifies alternative strategies to be used to ensure project success if specified risk events occur.
Contingency Reserve
(Context: Project Management)
Definition
The amount of funds, budget, or time needed above the estimate to reduce the risk of overruns of project objectives to a level acceptable to the organization.
Continuity of Operations Plan (COOP)
(Context: General, Technology Management)
Definition
A set of documented procedures developed to provide for the continuance of essential business functions during an emergency.
What is the difference between a HVA, BIA, and a COOP Plan? HHS.gov
Continuity of Operations Planning
(Context: General, Technology Management)
Definition
The process of developing plans and procedures to continue the performance of essential business functions in the event of a business interruption or threat of interruption.
Continuous Delivery (CD)
(Context: Software)
Definition
(CI/CD) Continuous integration is focused on automatically building and testing code, as compared to continuous delivery, which automates the entire software release process up to production. Generally, incorporating both resolves to a set of software development practices that automate the process of building, testing, and deploying code changes frequently, ensuring that new features and bug fixes are quickly integrated into a shared code repository and readily available for release to production environments.
Continuous Integration (CI)
(Context: Software)
Definition
(CI/CD) Continuous integration is focused on automatically building and testing code, as compared to continuous delivery, which automates the entire software release process up to production. Generally, incorporating both resolves to a set of software development practices that automate the process of building, testing, and deploying code changes frequently, ensuring that new features and bug fixes are quickly integrated into a shared code repository and readily available for release to production environments.
Contract
(Context: General)
Definition
When used as a noun in this manual, contract refers to an agreement enforceable by law, between two or more competent parties, to do or not to do something not prohibited by law, for a consideration. A contract is any type of agreement or order for the procurement of goods or services. As a verb, contract has its usual legal sense, signifying the making of an agreement for consideration.
COV Vendors Manual - p27 of 101 pages
Contract Administration
(Context: General)
Definition
The management of all facets of a contract to assure the Contractor’s total performance is in accordance with the contractual commitments and that the obligations of the Contractor under the terms and conditions of the contract are fulfilled.
Contract Closure
(Context: General, Project Management)
Definition
ITRM - The process of terminating contracts with external organizations or businesses.
These contracts may be vehicles for providing technical support, consulting, or any number of services supplied during the project that the agency decided not to perform with internal resources. Contracts can be brought to closure for a variety of reasons, including contract completion, early termination, or failure to perform. Contract closure is a typical but important part of project management. It is a simple process, but close attention should be paid so that no room is left for liability of the agency.
PMBOK - The process of completing and settling the contract, including resolution of any open items and closing each contract.
Contract, Cost-Plus-A-Fixed-Fee
(Context: General)
Definition
A cost-reimbursement type contract that provides for the payment of a fixed fee to the contractor. The fixed fee, once negotiated, does not vary with the actual cost but may be adjusted as a result of any subsequent changes in the scope of work or services to be performed under the contract.
Contract, Cost-Plus-A-Percentage-Of-Cost
(Context: General)
Definition
A form of contract which provides for a fee or profit at a specified percentage of the contractor's actual cost of accomplishing the work. Except in case of emergency affecting the public health, safety or welfare and for some insurance contracts, no public contract shall be awarded on the basis of cost plus a percentage of cost (Code of Virginia, § 2.2- 4331).
Contract, Fixed Price
(Context: General)
Definition
A contract that provides for a firm unit or total price to be established at the time of order placement or contract award. The contractor bears the full risk for profit or loss.
Contract, Fixed Price with Escalation/De-escalation
(Context: General)
Definition
A fixed price type of contract that provides for the upward and downward revision of the stated contract price upon the occurrence of certain contingencies (such as fluctuations in material costs and labor rates) defined explicitly in the contract.
Control
(Context: Project Management, Security)
Definition
(Context: Security) - Any protective action, device, procedure, technique or other measures that reduces exposures. Types of controls include preventative, detective, corrective, etc.
(Context: Project Management) - Comparing actual performance with planned performance, analyzing variances, assessing trends to effect process improvements, evaluating possible alternatives, and recommending appropriate corrective action as needed.
Control And Provisioning of Wireless Access Points (CAPWAP)
(Context: Data Center Facility, Hardware)
Definition
This protocol is under development within the IETF to enable an Access Controller (AC) to manage a collection of Wireless Termination Points (WTPs). CAPWAP aims at simplifying the deployment and control of large-scale, possibly heterogeneous, wireless networks.
Control Charts
(Context: Project Management)
Definition
A graphic display of process data over time and against established control limits, and that has a centerline that assists in detecting a trend of plotted values toward either control limits.
Control Item
(Context: Project Management)
Definition
A project element that is considered a unit for the purpose of change and configuration management. This includes such items as software modules, versions of software systems, the project design document, the project plans, and so forth.
Control Objectives for Information and related Technology (COBIT)
(Context: Technology Management)
Definition
A framework of best practices for IT management that provides managers, auditors, and IT users with a set of generally accepted measures, indicators, processes and best practices to assist them in maximizing the benefits derived through the use of information technology and developing appropriate IT governance and control.
Control System
(Context: Project Management)
Definition
A mechanism that reacts to the current project status in order to ensure accomplishment of project objectives.
Cookies
(Context: General)
Definition
Information stored on a Website visitor's computer regarding a transaction with a Website that may be returned to that Website at each subsequent visit if requested by the Website.
Core Processes
(Context: Project Management)
Definition
Processes that have clear dependencies and that require the same order on most projects.
Corrective Action
(Context: Project Management)
Definition
Documented direction for executing the project work to bring expected future performance of the project work in line with the project management plan.
Cost Avoidance
(Context: Technology Management)
Definition
An action taken in the present design to decrease costs in the future.
Cost Benefit Analysis (CBA)
(Context: Technology Management)
Definition
An evaluation of the costs and benefits of alternative approaches to a proposed activity to determine the best alternative.
How to Do a Cost-Benefit Analysis & Why It’s Important - Harvard Business School Online
Cost Budgeting
(Context: Project Management)
Definition
The process of aggregating the estimated costs of individual activities or work packages to establish a cost baseline.
Cost Control
(Context: Project Management)
Definition
The process of influencing the factors that create variances and controlling changes to the project budget.
Cost Effectiveness Analysis (CEA)
(Context: General, Technology Management)
Definition
A systematic quantitative method for comparing the costs of alternative means of achieving the same stream of benefits or a given objective.
Cost Estimating
(Context: Project Management)
Definition
The process of developing an approximation of the cost of the resources needed to complete project activities.
Cost of Quality
(Context: Project Management)
Definition
Determining the costs incurred to ensure quality.
Cost Performance Index (CPI)
(Context: Project Management)
Definition
A measure of cost efficiency on a project. It is the ratio of earned value (EV) to actual costs (AC). CPI = EV divided by AC. A value equal to or greater than one indicates a favorable condition and a value less than one indicates an unfavorable condition.
Cost Reimbursable Contracts
(Context: General, Technology Management)
Definition
This category of contract involves payment (reimbursement) to the contractor for its actual costs. Costs are usually classified as direct costs (costs incurred directly by the project, such as wages for members of the project team) and indirect costs (costs allocated to the project by the performing organization as a cost of doing business, such as salaries for corporate executives). Indirect costs are usually calculated as a percentage of direct costs. Cost reimbursable contracts often include incentives for meeting or exceeding selected project objectives such as schedule targets or total cost.
Cost Variance (CV)
(Context: Project Management)
Definition
A measure of cost performance on a project. It is the algebraic difference between earned value (EV) and actual cost (AC). CV=EV minus AC. A positive value indicates a favorable condition, and a negative value indicates an unfavorable condition.
Cost/Schedule Impact Analysis (CSIA)
(Context: Project Management)
Definition
The process followed to determine the cost and/or schedule impact of a specific change with a project.
Countermeasure
(Context: Information Systems Security)
Definition
An action, device, procedure, technique, or other measure that reduces vulnerability or the impact of a threat to an information system.
COV 4-2-1-1 Backup Rule
(Context: Technology Management)
Definition
A modernized version of the 3-2-1 backup rule, that provides additional safeguards and recovery options in the event of a ransomware attack or other hardware media failure. This includes at least 4 copies of data (including production), utilizing 2 backup methodologies/media types, 1 offsite copy for DR, and 1 offline cyber resilient backup.
EA-Solution-Data-Availability-Requirements.pdf (virginia.gov)
COV Data
(Context: Technology Management)
Definition
Data maintained, transformed or stored by an agency or its designee in the performance of Commonwealth business.
https://www.vita.virginia.gov/media/vitavirginiagov/it-governance/ea/pdf/EA-Smart-Device-Use.pdf
COV Data Protection
(Context: Commonwealth Data Management Program, Information Systems Security)
Definition
Protects from loss of data or loss of access to data in case of unforeseen events such as hardware or software failures in the storage systems, server failures, power loss or external events. Data Protection is a multi-layered approach designed to achieve, 2 objectives; (a) prevent data loss and (b) recover from data loss. Backup and/or replication are methods used to provide “extra copies” to recover (objective b).
COV Data Retention
(Context: Commonwealth Data Management Program, Technology Management)
Definition
Provides the capability for customers to retain non-current data to meet business requirements. Data retention requirements depend on the content of the data, whether the contents are classified as public records, and agency policies and business requirements.
COV Data Vaulting
(Context: Information Systems Security, Software)
Definition
The commonwealth's data safeguarding architecture and methods for providing a cyber-resilient backup service. The COV Data Vault service will be secure from ransomware attacks. The backups within the vault will be either off-line, air-gapped or will be otherwise isolated from the COV network in such a way that the backup is unable to be changed (immutable).
EA-Solution-Data-Availability-Requirements.pdf (virginia.gov)
COV Smart Device
(Context: Technology Management)
Definition
Any COV purchased smart device that is used to connect to a COV network, or to another smart device authenticated to a COV network, which: 1) Can store COV data; 2) Can be managed through MDM; 3) Has been issued and authorized by an agency for a COV employee.
https://www.vita.virginia.gov/media/vitavirginiagov/it-governance/ea/pdf/EA-Smart-Device-Use.pdf
COV Web System
(Context: General, Hardware, Software)
Definition
Any web system created by, or on behalf of, a Commonwealth agency that is deployed on COV-based infrastructure, hosted on a media platform, or is downloadable for installation on smart devices, including:
- Web applications created by agency development teams or 3rd party vendors
- Web sites created on platform systems[1]
- Low-code/No-Code applications[2]
- Web apps for smart devices
- Web-based desktop systems[3]
EA-Solutions-Web-Systems-Standard.pdf
[1] Examples include systems such as T4, Oracle Financials, or Salesforce.
[2] Examples include systems such as Microsoft Power Apps or AWS Honeycode.
[3] Examples include systems constructed in the manner of Microsoft Teams or Slack.
COV-HIE1
(Context: )
Definition
The COV-HIE is a network and a service, and exchange within its name is both a noun and a verb. As a noun, it is a digital network allowing providers to exchange electronically and with semantic interoperability health care data about patients they share. As a verb, it is a collection of services that reliably communicate clinical data between providers by identifying patients and locating their digital medical records across various electronic medical record systems.
COV-Registered Phone
(Context: Technology Management)
Definition
A personally owned phone registered with VCCC for serving as the second factor in a two-factor authentication transaction. A registered phone may be any device capable of receiving phone calls, including smartphones, call-only mobile phones, or landline phones. The phone is not necessarily a BYOD smart device but may be used as one if it meets the definition.
https://www.vita.virginia.gov/media/vitavirginiagov/it-governance/ea/pdf/EA-Smart-Device-Use.pdf
CPI
(Context: )
Definition
Common Program Interface. IBM’s Systems Application Architecture API.
Crashing
(Context: Project Management)
Definition
A specific type of project schedule compression technique performed by taking action to decrease the total project schedule duration after analyzing a number of alternatives to determine how to get the maximum duration compression for the lease additional cost. Typical approaches for crashing a schedule include reducing schedule activity duration and increasing the assignment of resources on schedule activities.
Crawlable Website
(Context: General)
Definition
A web site whose content is accessible by search engines so the content can be indexed.
A crawler follows the links on the web. A crawler is also called a robot, a bot, or a spider. It goes around the internet 24/7. Once it comes to a website, it saves the HTML version of a page in a gigantic database, called the index. This index is updated every time the crawler comes around your website and finds a new or revised version of it.
Alternative "non-crawable" website. No indexing occurs.
Credential
(Context: Information Systems Security)
Definition
Information, such as a user ID and password passed from an information system or information system user to an information system to establish access rights
Critical Activity
(Context: Project Management)
Definition
Any schedule activity on a critical path in a project schedule. Most commonly determined by using the critical path method. Although some activities are "critical" in the dictionary sense, without being on the critical path, this meaning is seldom used in the project context.
Critical Infrastructure
(Context: Hardware)
Definition
System and assets, whether physical or virtual, so vital to operations that the incapacity or destruction of such systems and assets would have a debilitating impact to economic security, public health or safety, or any combination of those matters.
Critical Path
(Context: Project Management)
Definition
Generally, but not always, the sequence of schedule activities that determines the duration of the project. Generally, it is the longest path through the project. However, a critical path can end, as an example, on a schedule milestone that is in the middle of the project schedule and that has a finish-no-later-than imposed date schedule constraint.
PMBOK
Critical Path Method (CPM)
(Context: Project Management)
Definition
A schedule network analysis technique used to determine the amount of scheduling flexibility (the amount of float) on various logical network paths in the project schedule network, and to determine the minimum total project duration. Early start and finish dates are calculated by means of a forward pass using a specified start date. Late start and finish dates are calculated by means of a backward pass, starting from a specified completion date, which sometimes is the project early finish date determined during the forward pass calculation.
PMBOK
Critical Success Factors
(Context: Project Management)
Definition
The limited number of areas of performance that are essential for a project to achieve its goals and objectives. They are the key areas of activity in which favorable results are absolutely necessary to reach goals. Critical success factors are often referred to as "CSF".
Role of project maturity and organizational culture on project success
Criticality
(Context: Information Systems Security)
Definition
Each log category has an assigned criticality level based on its relative cybersecurity value. This cybersecurity value relates to the usefulness of the log data for threat detection, with the data of the highest value assigned a criticality of zero, and the lowest a criticality of 3.
https://www.vita.virginia.gov/media/vitavirginiagov/it-governance/ea/pdf/Event-Log-Management.pdf
Cryptography
(Context: Information Systems Security)
Definition
The process of transforming plain text into cipher text, and cipher text into plain text.
Sources: NIST SP 800-20 under Encryption; NIST SP 800-67 Rev. 2 under Encryption
Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS)
(Context: General)
Definition
A measure of the largest burst of layout shift scores for every unexpected layout shift that occurs during the entire lifespan of a page.
Current Finish Date
(Context: Project Management)
Definition
The current estimate of the point in time when a schedule activity will be completed, where the estimate reflects any reported work progress.
PMBOK
Current Start Date
(Context: Project Management)
Definition
The current estimate of the point in time when a schedule activity will begin, where the estimate reflects any reported work progress.
PMBOK
Customer
(Context: Project Management)
Definition
The person or organization that will use the project's product or service or results.
PMBOK
Client/Customer - The Complete Glossary of Project Management Terminology
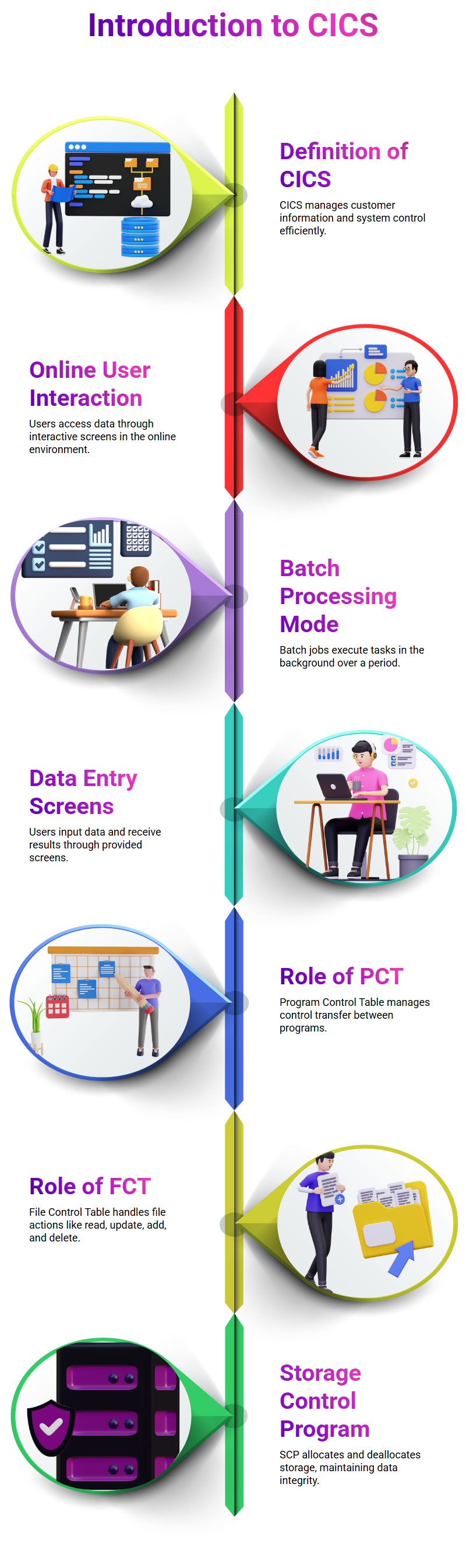
Customer Information Control System (CICS)

(Context: Hardware)
Definition
IBM® CICS® Transaction Server is a family of scalable general-purpose transaction processing solutions for z/OS, VSE/ESA, and distributed platforms. These servers support large transaction volumes with fast, consistent response times and provide high availability and scalability at a low cost per transaction.
CICS manages the sharing of resources, the integrity of data and prioritization of execution, with fast response. CICS authorizes users, allocates resources (real storage and cycles), and passes on database requests by the application to the appropriate database manager (such as DB2). We could say that CICS acts like and performs many of the same functions as the z/OS operating system.
Customer to government (C2G)
(Context: General)
Definition
Refers to a business process involving electronic interaction of citizens with government.
Cyber Resilience
(Context: Information Systems Security, Technology Management)
Definition
The ability of an organization to enable business acceleration (enterprise resiliency) by preparing for, responding to, and recovering from cyber threats. A cyber-resilient organization can adapt to known and unknown crises, threats, adversities, and challenges. Critical data is routinely monitored and tested for integrity, and recoverability.
EA-Solution-Data-Availability-Requirements.pdf (virginia.gov)
Cyber Resilient Backup
(Context: Software, Technology Management)
Definition
A backup of critical data often “air-gapped” that is routinely monitored and tested for integrity, and recoverability.
EA-Solution-Data-Availability-Requirements.pdf (virginia.gov)
Cyber Security
(Context: Information Systems Security)
Definition
Practice of defending computers, servers, mobile devices, electronic systems, networks, and data from malicious attacks. It's also known as information technology security or electronic information security.
EA-Solution-Data-Availability-Requirements.pdf (virginia.gov)
