Find keyword or terms by letter
Click on a numbered or lettered box below to show list of keywords and terms.
Academic Instruction and Research Systems
(Context: Hardware, Information Systems Security, Software)
Definition
Academic instruction and research systems, as noted in the ISO 27002 Security Standard, are defined as those systems used by institutions of higher education for the purpose of providing instruction to students or faculty for the purpose of conducting research. Per ISO 27002, section 1.6c, academic instruction or research systems are explicitly exempt from complying with the ISO 27002 standards.
Acceptance Criteria
(Context: Project Management, Technology Management)
Definition
Those criteria, including performance requirements and essential conditions, which must be met before project deliverables are accepted.
Accessible Rich Internet Applications (ARIA)

(Context: Software, Technology Management)
Definition
A technical specification published by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) that specifies how to increase the accessibility of web pages dynamic content, and user interface components developed with Ajax, HTML, JavaScript, and related technologies.
EA Solutions Web Systems Standard
Accessible Rich Internet Applications (WAI-ARIA) 1.2.
WAI-ARIA Overview | Web Accessibility Initiative (WAI) | W3C
ACMS
(Context: Software)
Definition
A transaction processing monitor from Compaq that runs on the open VMS operating system. May be either the Compaq ACMS for OpenVMS Alpha or the Compaq ACMS for OpenVMS VAX.
Compaq ACMS for OpenVMS Knowledge Modules - December 1999 (hpe.com)
Acquisition Process
(Context: General)
Definition
The process of acquiring personnel/goods/services for new or existing work within the general definitions of contracts requiring an offer and acceptance, consideration, lawful subject matter, and competent parties.
Action Item Status
(Context: Project Management)
Definition
A list of problem issues, including a description, point of contact, and dates of action and resolution.
How to Create Action Items & Action Item Lists: Tracker Included - ProjectManager
Action Plan
(Context: General, Project Management)
Definition
A plan that describes what needs to be done and when it needs to be completed. Project plans are action plans.
How to Write an Action Plan (Example Included) - ProjectManager
2023-Strategy-to-Action-Plan-Added-April-2024.pdf (virginia.gov)
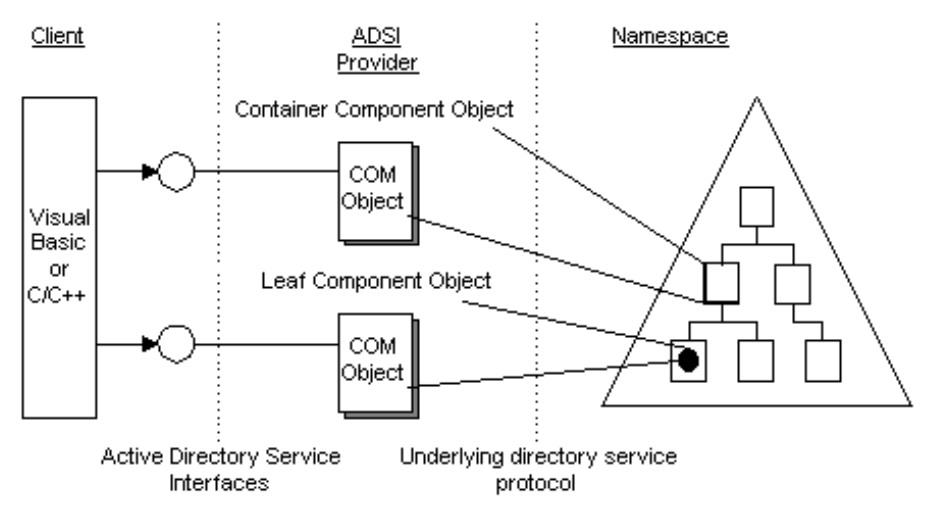
Active Directory Service Interfaces (ADSI)

(Context: Security, Software, Technology Management)
Definition
ADSI abstract the capabilities of different directory services from different network vendors to present a single set of directory service interfaces for managing network resources.
It is a set of COM interfaces used to access the features of directory services from different network providers. ADSI is used in a distributed computing environment to present a single set of directory service interfaces for managing network resources. Administrators and developers can use ADSI services to enumerate and manage the resources in a directory service, no matter which network environment contains the resource. ADSI enables common administrative tasks, such as adding new users, managing printers, and locating resources in a distributed computing environment.
Integration-Domain-Report.pdf (virginia.gov)
Active Directory Service Interfaces - Win32 apps | Microsoft Learn
Active Projects
(Context: Project Management)
Definition
A project portfolio category for Commonwealth-level IT projects that have been granted Project Initiation approval by the appropriate approval authority.
Active Storage
(Context: Technology Management)
Definition
Refers to data that is stored in a manner that facilitates frequent use and ease of access.
https://www.vita.virginia.gov/media/vitavirginiagov/it-governance/ea/pdf/Event-Log-Management.pdf
ActiveX
(Context: Software)
Definition
1. Microsoft's answer to Java. ActiveX is a stripped-down implementation of OLE designed to run over slow Internet links.
2. ActiveX is a deprecated software framework created by Microsoft that adapts its earlier Component Object Model (COM) and Object Linking and Embedding (OLE) technologies for content downloaded from a network, particularly from the World Wide Web. Microsoft introduced ActiveX in 1996. In principle, ActiveX is not dependent on Microsoft Windows operating systems, but in practice, most ActiveX controls only run on Windows. Most also require the client to be running on an x86-based computer because ActiveX controls contain compiled code. ActiveX is still supported in the "Internet Explorer mode" of Microsoft Edge (which has a different, incompatible extension system, as it is based on Google's Chromium project).
3. ActiveX is a model for writing programs so that other programs and the operating system can call them. ActiveX technology is used with Microsoft Internet Explorer to make interactive Web pages that look and behave like computer programs, rather than static pages. With ActiveX, users can ask or answer questions, use push buttons, and interact in other ways with the Web page. ActiveX controls are often written using Visual Basic. Active X is notable for a complete lack of security controls; computer security experts discourage its use over the Internet.
1. Integration-Domain-Report.pdf (virginia.gov)
Activity
(Context: General, Project Management)
Definition
1. An activity is generally the smallest portion of a project used in planning, tracking, and control. In some projects, activities may be referred to as tasks, stories, work packages, or use cases, or using other descriptors.
2. Set of cohesive tasks of a process.
2. NIST SP 800-160v1r1 from ISO/IEC/IEEE 15288:2015
Activity Duration
(Context: Project Management)
Definition
The time in calendar units between the start and finish of a scheduled activity.
Activity Duration - Project Management Knowledge (project-management-knowledge.com)
Activity Duration Estimating
(Context: Project Management)
Definition
Represents the act of quantifying the amount of time that it is anticipated the activity will take to complete.
Activity Duration Estimating - Project Management Knowledge (project-management-knowledge.com)
Activity Resource Estimating
(Context: Project Management)
Definition
The main purpose of the activity resource estimating process is to determine the resource requirements for each activity, and therefore this is the major output item from this process. You identify the types of resources required to perform each activity and estimate the required quantity of each identified resource. If a work package in the WBS has multiple activities, the resource estimates for those activities can be aggregated to estimate the resource requirements for the work package. The requirement documents may also include information such as the basis for each estimate, the assumptions made for the estimate, and the availability of the resources.
Actual Cost (AC)
(Context: Project Management)
Definition
The actual cost of a project represents the true total and final costs accrued during the process of completing all work during the pre-determined period of time allocated for all schedule activities as well as for all work breakdown structured components.
Actual costs are primarily made up of a number of specific items including, but not limited to, cost in direct labor hours, direct costs alone, and also all costs including indirect costs. Actual costs, when possible, should be thoroughly itemized in detail throughout the project as opposed to merely compiled at the end as it is easier to accurately itemize costs when it is done as the expenditures occur. The term actual cost can also be referred to as actual costs of work performed (AWCP).
For more information on the term actual cost, see the definitions for earned value management as well as the definition for earned value technique.
Actual Cost - Project Management Knowledge (project-management-knowledge.com)
Also referred to as the .
Become a Certified Project Manager: Search results for actual costs (getpmpcertified.blogspot.com)
Actual Cost of Work Performed (ACWP)
(Context: Project Management)
Definition
This is the total cost actually incurred until a specific point on the timeline in performing the work for a project.
Administrative Closure
(Context: Project Management)
Definition
This is the final completion and closure of the project. Part of the Integration Management knowledge area, the Close Project or Phase process is done when all the work has been verified, delivered, and accepted by the customer. All open issues have been raised and finalized (come to a conclusion and closure).
Difference between Administrative Closure & Contract Closure | PMChamp

Advanced Mobile Phone Service (AMPS)

(Context: General)
Definition
Defined in EIA/TIA-553 standards. In 2006, AMPS is still the most extensive wireless coverage available for nationwide service in the US. However, in 2002, the FCC made the drastic decision to no longer require A and B carriers to support AMPS cellular service as of March 1, 2008. Since the AMPS standard is analog technology, it suffers from an inherently inefficient use of the frequency spectrum. All AMPS carriers have converted most of their consumer base to a digital standard such as CDMA or GSM and continue to do so at a rapid pace. Digital technologies such as CDMA support multiple voice calls on the same channel, superior call quality, enhanced features such as two-way text messaging, voicemail indicator, internet, and GPS services; whereas, AMPS can only support one call per channel and a basic one-way short message service. AMPS cellular service operates in the 800 MHZ FM band. In 1989, the Federal Communications Commission granted carriers an expansion from the current 666 channels to the now 832 (416 per carrier). The additional frequency was available in the upper 800 MHz band which also was home to UHF channels 70-83. This meant that these UHF channels could no longer be used for UHF TV transmission as these frequencies were to be used for AMPS transmission.
Agency
(Context: Enterprise Architecture, General)
Definition
1. "Executive branch agency" or "agency" means any agency, institution, board, bureau, commission, council, public institution of higher education, or instrumentality of state government in the executive department listed in the appropriation act. However, "executive branch agency" or "agency" does not include the University of Virginia Medical Center, a public institution of higher education to the extent exempt from this chapter pursuant to the Restructured Higher Education Financial and Administrative Operations Act (§ 23.1-1000 et seq.) or other law, or the Virginia Port Authority.
2. Any agency, institution, board, bureau, commission, council, or instrumentality of the Commonwealth of Virginia listed in the appropriation act. For purposes of Enterprise Architecture standards, "agency" includes the administrative functions (does not include instructional or research functions) of institutions of higher education, unless exempted by language contained in a specific requirement/standard.
3. "Agency" means an administrative unit of state government, including any department, institution, commission, board, council, authority, or other body, however designated.
1. Code of Virginia Code - Article 1. General Provisions
2.
Agency Banner
(Context: Technology Management)
Definition
For purposes of the Commonwealth of Virginia Web template, an "Agency Banner " is the graphic used between the "Commonwealth Banner" and the main content (on the home page template), or the "" and the lower breadcrumb bar (on the sub-page template).
The image is 100 pixels high and should gracefully handle resolutions at least as wide as 1024 pixels.
Agency Head
(Context: General)
Definition
The chief executive officer of a department established in the government of the Commonwealth of Virginia.
§ 2.2-106. Appointment of agency heads; disclosure of resumes; severance (virginia.gov)
https://www.dhrm.virginia.gov/docs/default-source/hr/manuals/agyheadhandbook.pdf?sfvrsn=4
Agency Information Technology Resource (AITR)
(Context: ITRM perspective, Technology Management)
Definition
The Code of Virginia requires the head of each executive branch agency to designate an existing employee to be the agency's information technology resource who shall be responsible for compliance with the policies, standards, and guidelines established by the Chief Information Officer of the Commonwealth.
The AITR shall:
- Serve as primary point of contact for the agency for VITA communiqués and distribute to all affected parties within the agency and if necessary working with communication staff in the agency
- Ensure that the agency IT investment information in the strategic plan is current and accurate
- The primary resource responsible for preparing the IT Strategic Plan is the agency information technology resource (AITR)
- Submit agency IT investments (projects and procurements) for approval to VITA
- Work collaboratively with VITA to resolve issues and concerns
Agency Management
(Context: General)
Definition
A term that refers to those people who are responsible for the business operations of an agency.
Agency-level Project
(Context: Project Management)
Definition
Projects with an Estimated Cost at Completion of less than $250,000 are considered to be agency-level projects, completely under the control of the agency's management.

Agile Development

(Context: Project Management, Software, Technology Management)
Definition
An iterative approach to project management and software development that uses incremental delivery, team collaboration, continual planning, and continual learning to deliver solutions. Based on the 2001 Manifesto for Agile Software Development, it promotes lean processes that focus on the construction of smaller sets of features and capabilities of a system that are reviewed with stakeholders at regular intervals. This shorter cycle of development and review facilitates a rapid response to change as priorities shift or new needs are identified.
Agile teams typically operate in sprints, short 2-3 week intervals in which a discrete set of features, called stories, are developed. An agile team meets daily for a short 15-minute checkpoint, called a stand up, to assess progress against stories, the completed results of which are demonstrated to project stakeholders at an end-of-sprint review.
Alert
(Context: General)
Definition
Notification that an event has occurred or may occur.
https://csrc.nist.gov/glossary/term/alert
https://niccs.cisa.gov/cybersecurity-career-resources/vocabulary
Alignment
(Context: General)
Definition
The degree of agreement, conformance, and consistency among organizational purpose, vision and values; structures, systems, and processes; and individual skills and behaviors.
GAO
https://www.gao.gov/assets/2019-11/aga_2.pdf (p17 of 27)
Alternative Analysis
(Context: Project Management, Technology Management)
Definition
Breaking down a complex situation for the purpose of generating and evaluating different solutions and approaches.
COV Project Management Standard CPM-112 (p24 of 58)
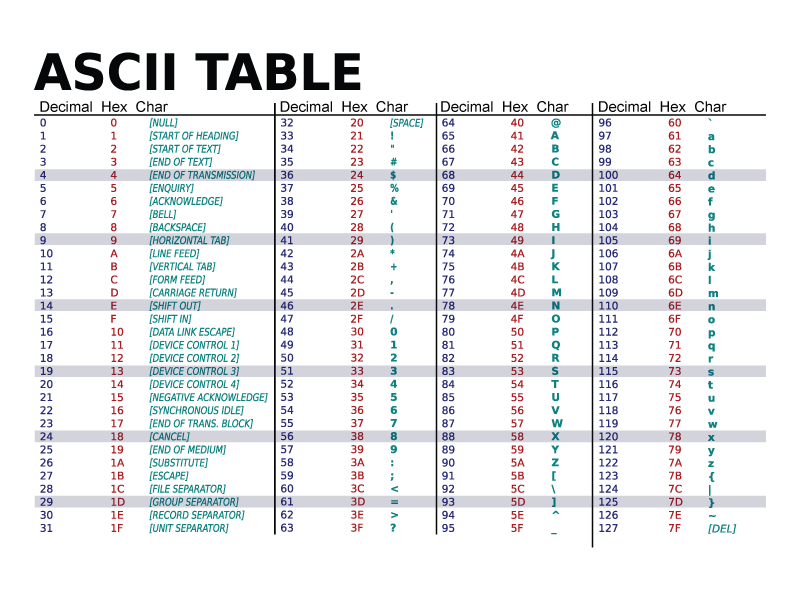
American Standard Code for Information Interchange (ASCII)

(Context: General, Software)
Definition
ASCII (American Standard Code for Information Interchange) is a standard character encoding used in telecommunication. The ASCII pronounced 'ask-ee', is strictly a seven-bit code based on the English alphabet. ASCII codes are used to represent alphanumeric data.
The code was first published as a standard in 1967. it was subsequently updated and published as ANSI X3.4-1968, then as ANSI X3.4-1977, and finally as ANSI X3.4-1986. Since it is a seven-bit code, it can at the most represent 128 characters. it currently defines 95 printable characters including 26 upper case letters (A to Z), 26 lower case letters, 10 numerals (0 to 9), and 33 special characters including mathematical symbols, punctuation marks, and space characters. They represent text in, telecommunications equipment, and devices. These include numbers, upper and lowercase English letters, functions, punctuation symbols, and some other symbols.
In total, there are 256 ASCII characters, and can be broadly divided into three categories:
- ASCII control characters (0-31 and 127)
- ASCII printable characters (32-126) (most commonly referred to)
- Extended ASCII characters (128-255)
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/what-is-ascii-a-complete-guide-to-generating-ascii-code/
ASCII Values Alphabets ( A-Z, a-z & Special Character Table ) - GeeksforGeeks
Analysis
(Context: General)
Definition
The detailed study and examination of something, in order to discover more about it (from Cambridge International Dictionary of English).
Analysis typically includes discovering parts of the item being studied, as well as how they fit together. An example is the study of schedule variances for cause, impact, corrective action, and results.
ANSI

(Context: General)
Definition
A voluntary non-profit organization that administers, coordinates, and supports the U.S. voluntary consensus standards and conformity assessment system.
American National Standards Institute - Wikipedia
APPC LU 6.2
(Context: Software)
Definition
APPC allows user written programs to perform transactions in a Client-Server IBM network to access a CICS, in MVS "batch" through APPC/MVS, in VM/CMS, in AIX on the RS/6000, and on the AS/400.
In computing, Advanced Program to Program Communication or APPC is a protocol which computer programs can use to communicate over a network. APPC is at the application layer in the OSI model, it enables communications between programs on different computers, from portables and workstations to midrange and host computers. APPC is defined as VTAM LU 6.2 ( Logical unit type 6.2 ).
Logical Unit 6.2 is an IBM-originated communications protocol specification dating from 1974, and is part of IBM's Systems Network Architecture (SNA). A device-independent SNA protocol, it is used for peer-to-peer communications between two systems, for example, between a computer and a device (e.g. terminal or printer), or between computers. LU6.2 is used by many of IBM's products, including Common Programming Interface for Communications Intersystem Communications (CICS ISC), and Information Management System, and also many non-IBM products.
IBM Advanced Program-to-Program Communication - Wikipedia
To verify server APPC/LU 6.2 settings via Control Center
Appliance
(Context: Hardware, Hosting Options)
Definition
Also known as a Computing Appliance or Hardware Appliance.
Generally, a separate and discrete hardware device with integrated software (firmware), specifically designed to provide a specific computing resource. These are generally "closed and sealed" – not serviceable by the owner. The hardware and software are pre-integrated and pre-configured before delivery to the customer, to provide a "turnkey" solution to a particular problem. Unlike general purpose computers, appliances are generally not designed to allow the customers to change the software (including the underlying operating system), or to flexibly reconfigure the hardware.
Definition of Computing Appliance - Gartner Information Technology Glossary
Appliance Server (also Server Appliance)
(Context: Hardware)
Definition
A specialized device designed for ease of installation and maintenance, which fulfills the traditional functions of an application, database, or web server. Purchased from a single vendor, these servers are delivered as a complete unit, with all of the required hardware and software components pre-installed and configured. It is intended to begin work almost immediately when attached to a network, with little additional configuration required.
Definition of Server Appliance - Gartner Information Technology Glossary
What is Server Appliance? | Webopedia
why should i use a physical server appliance? - Google Search
Application
(Context: Software)
Definition
An automated solution (computer program) designed to fulfill one or more business functions. It may be a single program designed for a single business function, or it may be a multi-module/program or multi-sub-system entity with modules/programs/components that support multiple business functions. An application may be purchased (COTS), custom- developed in-house, or reused from another entity.
What Is an Application? Definition from SearchSoftwareQuality (techtarget.com)
Application Area
(Context: Project Management)
Definition
A category of projects that have common components significant in such projects, but are not needed or present in all projects. Application areas are usually defined in terms of either the product (i.e., by similar technologies or production methods) or the type of customer (e.g., internal vs. external, government vs. commercial) or industry sector (i.e., utilities, automotive, aerospace, information technologies). Application areas often overlap.
Application Area (brainbok.com)
Application Area - Project Management Knowledge (project-management-knowledge.com)
Application Monitoring Dashboard
(Context: General)
Definition
A system that provides information about the metrics, usage, and performance of an application. Agencies should use a dashboard suited to the version, type, and deployment method of each application.
https://www.vita.virginia.gov/media/vitavirginiagov/it-governance/ea/pdf/Event-Log-Management.pdf

Application Programming Interface (API)

(Context: Software)
Definition
An interface that a software program implements in order to allow other software to interact with it, much in the same way that software might implement a user interface in order to allow humans to use it. APIs are implemented by applications, libraries and operating systems to define how other software can make calls to or request services from them.[1][2][3] An API determines the vocabulary and calling conventions the programmer should employ to use the services. It may include specifications for routines, data structures, object classes, and protocols used to communicate between the consumer and implementer of the API.
Definition of Application Programming Interface (API) - Gartner Information Technology Glossary
Application System
(Context: Software)
Definition
An interconnected set of information resources under the same direct management control that meets a defined set of business needs.
Application, Support System, and Information Technology (IT) System.
Approve
(Context: Project Management)
Definition
To accept as satisfactory. Approval implies that the item approved has the endorsement of the approving entity. The approval may still require confirmation by somebody else, as in levels of approval. In management use, the important distinction is between approved and authorized. See authorization.
SECTION 1 (michigan.gov) p4 of 23
Architectural Significance
(Context: Enterprise Architecture)
Definition
A concern, problem, or system element that has a wide impact on the structure of a system, or on its important quality properties such as performance, scalability, security, reliability, or evolvability.
Architecture Overview Document (AOD)
(Context: Enterprise Architecture)
Definition
The Architecture Overview Document (AOD) templates help suppliers document their architectures in a way that reviewers can determine if the architecture is in compliance. The Architecture Overview Document (AOD) is split into 3 sections to be completed at different times in the lifecycle of service deployment. Each architecture will include a High-Level Section (HLS), a Detailed Design Section (DDS), and an As Built Section (ABS).
- HLS - Is a high-level section that is required to be approved prior to starting the project to build the architecture.
- DDS - Contains the information needed to build or rebuild the system and needs to be completed prior to service going live. It contains not only the system configuration, but also the configurations from any other suppliers that they need to do to bring your system online.
- ABS - Contains any variances from the Detailed Design and their configurations. It needs to be completed prior to project closeout.
ARDIS
(Context: )
Definition
A company that provides a cellular packet-switched radio data service in the U.S. Now completely owned by Motorola. (It used to be a joint venture with IBM.) Initially (1984), the network was designed by Motorola for IBM field service technicians. The radio protocol is proprietary (designed by IBM and Motorola). Has about 34,000 subscribers, about 10 times the number that RAM Mobile has. Data transmission is at 4,800 bits/s (using 240-byte packets, resulting in about 2,000 to 3,000 bits/s of user-data throughput) or 19,200 bits/s (in larger U.S. centers) using 512-byte packets, resulting in up to 8,000 bits/s of user-data throughput. Usage charges are per kbyte of data transferred. Sometimes called Datatac. Competes with RAM Mobile Data's Mobitex system and CDPD. Ardis is at http://www.ardis.com/. (Taken from O’Reilly)
Areas of Responsibility
(Context: Project Management)
Definition
Used to define the person or organizational entity responsible for specific policy areas, processes, and procedures as identified.
SECTION 1 (michigan.gov) p4 of 23
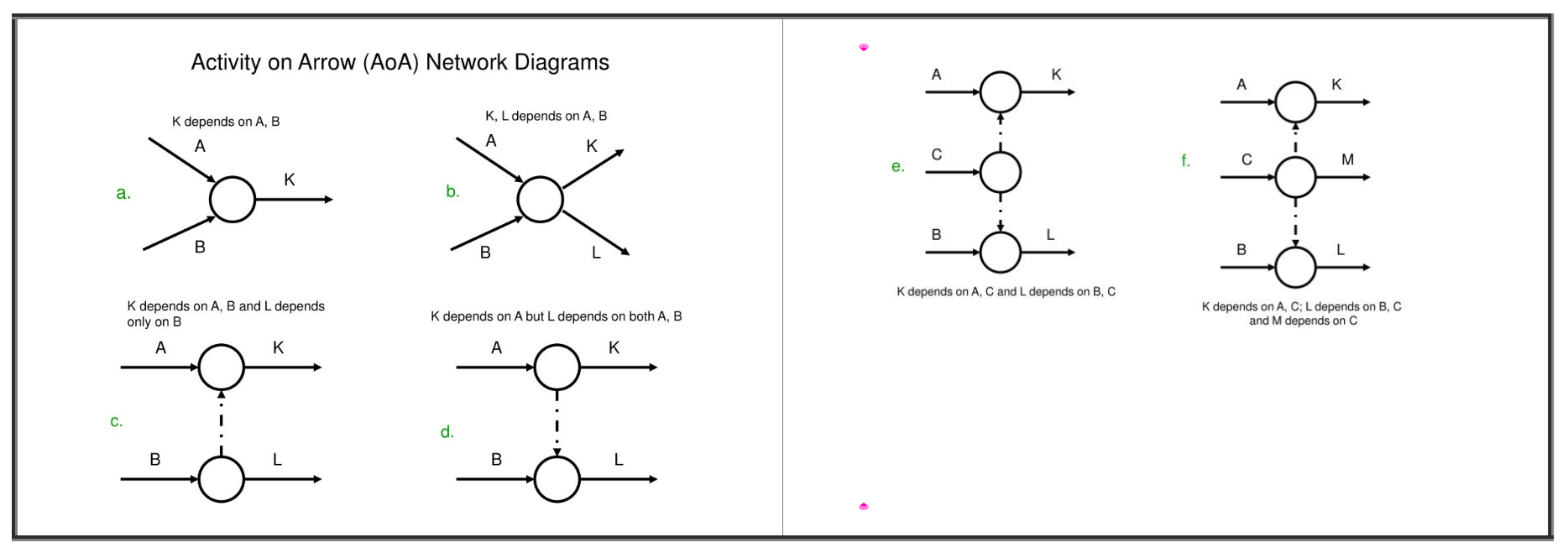
Arrow Diagramming Method (ADM)

(Context: Project Management)
Definition
A schedule network diagramming technique in which schedule activities are represented by arrows. The tail of the arrow represents the start, and the head represents the finish of the scheduled activity. Schedule activities are connected at points called nodes (usually drawn as small circles) to illustrate the sequence in which the schedule activities are expected to be performed.
SECTION 1 (michigan.gov) p4 of 23

Artificial Intelligence (AI)

(Context: Technology Management)
Definition
1. The simulation of human intelligence processes by machines, especially computer systems, such that it can adapt and learn on its own using machine learning algorithms that can analyze large volumes of training data to identify correlations, patterns, and other metadata that can be used to develop a model that can make predictions or recommendations based on future data inputs.
2. Refers to the simulation of human intelligence in machines that are programmed to think like humans and mimic their actions.
1. Artificial Intelligence | Virginia IT Agency
2. EA-Solution-Data-Availability-Requirements.pdf (virginia.gov)
As-A-Service
(Context: Hosting Options)
Definition
A technology solution where (1) the management of all layers beneath the offering in the technology stack is the responsibility of the service provider and (2) the pricing is metered or subscription-based. Also known as "X as a Service" or "* as a Service".
As-Built Section (ABS)
(Context: Enterprise Architecture, General, Technology Management)
Definition
VITA EA: Architecture Overview Document (AOD) is split into 3 sections to be completed at different times in the lifecycle of service deployment. Each architecture will include a High-Level Section (HLS), Detailed Design Section (DDS), and an As Built Section (ABS). As-Built Section (ABS) - Contains any variances from the Detailed Design Section (DDS) and their configurations. It needs to be completed prior to project closeout. Ideally this section is just a check off of the approved design, but sometimes there is a reason to vary from it. The purpose of this section is to capture variations from the approved architecture and designs so that if there is a need to rebuild this system from scratch, we have the knowledge.
General: A description of the state of an IT system as implemented. Where a provides the technical specification of a system to be constructed, an As-Built Document outlines the deployed system in detail, including hardware specifications, serial numbers, MAC & WWN addresses, host and domain names, software versions, patch levels, configuration settings, and system resources. It is not a Runbook, which is a procedural guide for how to install and configure a system, and to maintain it at runtime.
As Built Document: Everything You Need To Know (harmony-at.com)
Asset
(Context: General, Technology Management)
Definition
Any software, data, hardware, administrative, physical, communications, or personnel resources.
Assumptions
(Context: Project Management)
Definition
Factors that, for planning purposes, are considered to be true, real, or certain without proof or demonstration.
Project Management Institute (PMI) Terms (certificationacademy.com)
Assurance
(Context: Information Systems Security)
Definition
Measurement of confidence in a control or activity.

Asynchronous Mirroring

(Context: Software)
Definition
Data to be stored are written synchronously (with acknowledgment to the application) to a cache resource and then written asynchronously (without acknowledgment) to a primary store and a mirrored (copy of the primary) store.
Asynchronous mirroring overview (netapp.com)
Asynchronous mirroring - IBM Documentation
How asynchronous mirroring works | System Manager 11.50.2 | Lenovo Docs
Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM)
(Context: General, Software)
Definition
A cell switching technology that transports data at high speeds in small, uniform cells (packets). ATM may be used in LAN and WAN communications.
Asynchronous/ Connectionless Communication
(Context: General, Software)
Definition
A program-to-program communication model that does not block any of the communicating partners and that allows for time independent interactions
Asynchronous Connectionless-Mode Service (Network Interface Guide) (oracle.com)
Connectionless Communications using the Asynchronous Transfer Mode (utwente.nl)
ATM/SONET
(Context: General, Software)
Definition
Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) cells carried over Synchronous Optical Network (SONET) packets.
Attachment
(Context: General, Software, Technology Management)
Definition
Attachments are files embedded within online communication channels such as emails, instant messages, or social networks. File attachments can come in any form, such as images, documents, or programs. A paper clip image often symbolizes the presence of attachments in messages.
Attachment - Definition | Trend Micro (US)
https://www.vita.virginia.gov/media/vitavirginiagov/it-governance/ea/pdf/Event-Log-Management.pdf
Attack
(Context: Information Systems Security)
Definition
An attempt to bypass security controls on an information system in order to compromise the data.
Authenticate
(Context: Information Systems Security)
Definition
Verifying the identity of a user, process, or device, often as a prerequisite to allowing access to resources in an information system.
To determine that something is genuine. To reliably determine the identity of a communicating party or device.Sources:
NIST SP 1800-10B under Authentication from FIPS 200
NIST SP 1800-21C under Authenticate
NIST SP 800-128 under Authentication from FIPS 200
NIST SP 800-137 under Authentication from FIPS 200
NIST SP 800-18 Rev. 1 under Authentication
NIST SP 800-30 Rev. 1 under Authentication from FIPS 200
NIST SP 800-39 under Authentication from FIPS 200
NIST SP 800-60 Vol. 1 Rev. 1 under Authentication from FIPS 200
NIST SP 800-60 Vol. 2 Rev. 1 under Authentication from FIPS 200Authentication
(Context: Information Systems Security)
Definition
The process of verifying an identity of a user to determine the right to access specific types of data or IT systems.
A security measure designed to protect a communications system against acceptance of fraudulent transmission or simulation by establishing the validity of a transmission, message, originator, or a means of verifying an individual's eligibility to receive specific categories of information.
Sources:
CNSSI 4009-2015 from CNSSI 4005, NSA/CSS Manual Number 3-16 (COMSEC)Authorization
(Context: Information Systems Security, Project Management, Technology Management)
Definition
(Context: Information Systems Security) - The process of granting access to data or information systems by the designated authority after proper identification and authentication.
(Context: Technology Management) - The power granted by management to specified individuals allowing them to approve transactions, procedures, or total systems.
(Context: Project Management) - In general, authorization is the power to make decisions that the management grants. The specific remit for authorization varies on a case-by-case basis.
Information Systems Security: authorization - Glossary | CSRC (nist.gov)
Project Management: The Complete Glossary of Project Management Terms |Smartsheet
Authorization Boundary
(Context: Information Systems Security)
Definition
All components of an information system to be authorized for operation by an authorizing official and exclude separately authorized systems, to which the information system is connected.
Authorized Work
(Context: Project Management)
Definition
An effort that has been approved by a higher authority and may or may not be defined.
Earned Value Management Best Practices Report (cms.gov)
The Complete Glossary of Project Management Terms |Smartsheet
Availability
(Context: Information Systems Security)
Definition
Protection of information systems and data so that they are accessible to authorized users when needed without interference or obstruction.
Availability Zone (AZ)
(Context: Data Center Facility, Technology Management)
Definition
An availability zone (AZ) is a subdivision within a cloud region that is designed to maximize fault tolerance and availability. AZs are made up of one or more data centers that are separated by significant distances, often miles apart. This separation reduces the likelihood that more than one AZ will be affected by a disaster, such as a power outage or natural disaster.
