Find keyword or terms by letter
Click on a numbered or lettered box below to show list of keywords and terms.
Validation
(Context: )
Definition
The technique of evaluating a component or product during or at the end of a phase or project to ensure it complies with the specified requirements. Contrast with verification.
PMBOK
Validator
(Context: )
Definition
A service or system that verifies that a page meets this Standard.
Variance
(Context: )
Definition
A quantifiable deviation, departure, or divergence away from a known baseline or expected value.
PMBOK
Vendor Independent Messaging (VIM)
(Context: )
Definition
A standard API for applications to integrate with e-mail on Windows 3.x, proposed by Lotus, Borland, IBM & Novell (CC:Mail.) in the early 1990s. Its main competitor was Microsoft's MAPI, which was the eventual winner of the MAPI v. VIM war
Verification
(Context: )
Definition
The technique of evaluating a component or product at the end of a phase or project to assure or confirm it satisfies the conditions imposed. Contrast with validation.
PMBOK
Version Control
(Context: )
Definition
The management of changes to documents, programs, and other data stored as computer files.
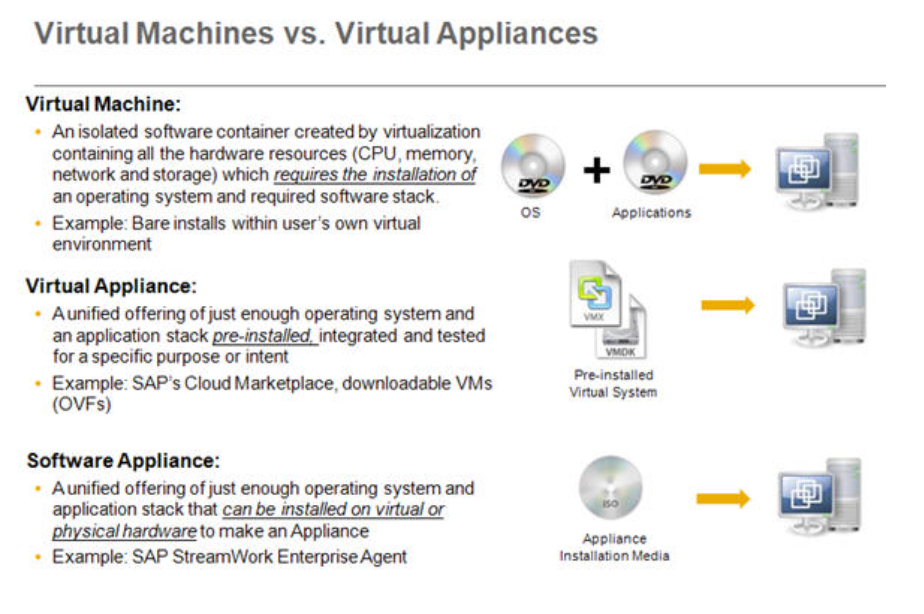
Virtual Appliance

(Context: )
Definition
A type of appliance that is a pre-configured virtual machine image that can be deployed on an existing customer hypervisor platform in order to perform its intended function.
Virtual Host
(Context: General)
Definition
On the Web, a server that contains multiple Web sites, each with its own domain name. As of the first version of the Web protocol (HTTP 1.0), each Web site on a virtual host must be assigned a unique IP address. HTTP Version 1.1 eliminates this requirement. See also virtual server.
Virtual Machine (VM)
(Context: General)
Definition
A software emulation of a physical computing environment. The term gave rise to the name of IBM's VM operating system whose task is to provide one or more simultaneous execution environments in which operating systems or other programs may execute as though they were running “on the bare iron”, that is, without an enveloping Control Program. A major use of VM is the running of both outdated and current versions of the same operating system on a single CPU complex for the purpose of system migration, thereby obviating the need for a second processor. (FOLDOC)
Virtual Private Network (VPN)
(Context: General)
Definition
A communications service that affords various levels of privacy over public or private infrastructure. Secure VPNs may use cryptographic tunneling protocols to preventing snooping, sender authentication to preventing identity spoofing, and message integrity (preventing message alteration) to achieve the privacy intended. Trusted VPNs do not use cryptographic tunneling. Instead, they rely on the security of a single provider's network to protect the traffic. Multi-protocol label switching (MPLS), layer 2 forwarding, and layer 2 tunneling are commonly used to build trusted VPNs.
Virtual Server
(Context: General)
Definition
1) Same as virtual host. (http://content.techweb.com/encyclopedia/)
2) A configuration of a World-Wide Web server that appears to clients as an independent server but which is actually running on a computer that is shared by any number of other virtual servers. Each virtual server can be configured as an independent web site, with its own hostname, content, and security settings. The Domain Name System or DNS maps the hostnames of all virtual servers on one physical server to its IP address. The web server software then uses the “Host” header in the HTTP request to determine which virtual server the request was for, and then processes the request using that virtual server's configuration. (foldoc.org)
3) Multiple servers that appear as one server, or one system image, to the operating system or for network administration.
http://content.techweb.com/encyclopedia/
Virtual Storage
(Context: General)
Definition
The storage space that may be regarded as addressable main storage by the user of a computer system in which virtual addresses are mapped into real addresses. The size of virtual storage is limited by the addressing scheme of the computer system and by the amount of auxiliary storage available, not by the actual number of main storage locations.
Virtual Tape
(Context: General)
Definition
The use of a special storage device that manages less-frequently needed data so that it appears to be stored entirely on tape cartridges when some parts of it may actually be located in faster, hard disk storage. The programming for a virtual tape system is sometimes called a virtual tape server (VTS). Virtual tape can be used with a hierarchical storage management (HSM) system in which data is moved as it falls through various usage thresholds to slower but less costly forms of storage media. Virtual tape may also be used as part of a storage area network (SAN) where less-frequently used or archived data can be managed by a single virtual tape server for a number of networked computers. A virtual tape system offloads from the main computer the processing involved in deciding whether data should be available in the faster disk cache or written onto a tape cartridge. The virtual tape system also can manage data so that more of the space on a tape cartridge is actually used. (searchStorage.com) IBM and Storage Technology are well-established vendors of virtual tape systems. Sutmyn Storage sells a product that provides a virtual interface to existing IBM and other systems.
Virus
(Context: Enterprise Architecture)
Definition
See Malicious Code
Vital Record
(Context: General)
Definition
A document, regardless of media, which, if damaged or destroyed, would disrupt business operations.
VM Snapshot
(Context: Software)
Definition
A backup type that generates a point in time copy of the virtual machine (vmdk file).
EA-Solution-Data-Availability-Requirements.pdf (virginia.gov)
Vocabulary
(Context: )
Definition
A code set, nomenclature system or identifier list maintained by an organization to standardize a particular domain (e.g., human genes, clinical terminology, provider identification).
Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP)
(Context: )
Definition
A service that permits voice connections and the transmission of voice conversations using IP packets that are sent over public and private cabled infrastructure. A set of equipment and protocols is required to accomplish quality voice communications using VoIP. A major advantage of VoIP and Internet telephony is that it avoids the tolls charged by ordinary telephone service. VoIP derives from the VoIP Forum, an effort by major equipment providers, including Cisco, VocalTec, 3Com, and Netspeak to promote the use of ITU-T H.323, the standard for sending voice (audio) and video using IP on the public Internet and within an intranet. The Forum also promotes the user of directory service standards so that users can locate other users and the use of touch-tone signals for automatic call distribution and voice mail. Using VoIP, an enterprise positions a “VoIP device” at a gateway. The gateway receives packetized voice transmissions from users within the company and then routes them to other parts of its intranet (local area or wide area network) or, using a T- carrier system or E-carrier interface, sends them over the public switched telephone network.
Voice over Wi-Fi (Vo-Fi) or wireless VoIP.
(Context: )
Definition
This is used successfully in hospitals or areas when no hand offs are needed.
Voice over Wireless LAN (VoWLAN)
(Context: )
Definition
An implementation of Voice over IP using wireless rather than wired infrastructure.
VPN
(Context: )
Definition
A network that uses a public telecommunication infrastructure, such as the Internet, to provide remote offices or remote users with secure access to their organization's network.
Vulnerability
(Context: )
Definition
A condition or weakness in security procedures, technical controls, or operational processes that exposes the system to loss or harm.
