Find keyword or terms by letter
Click on a numbered or lettered box below to show list of keywords and terms.
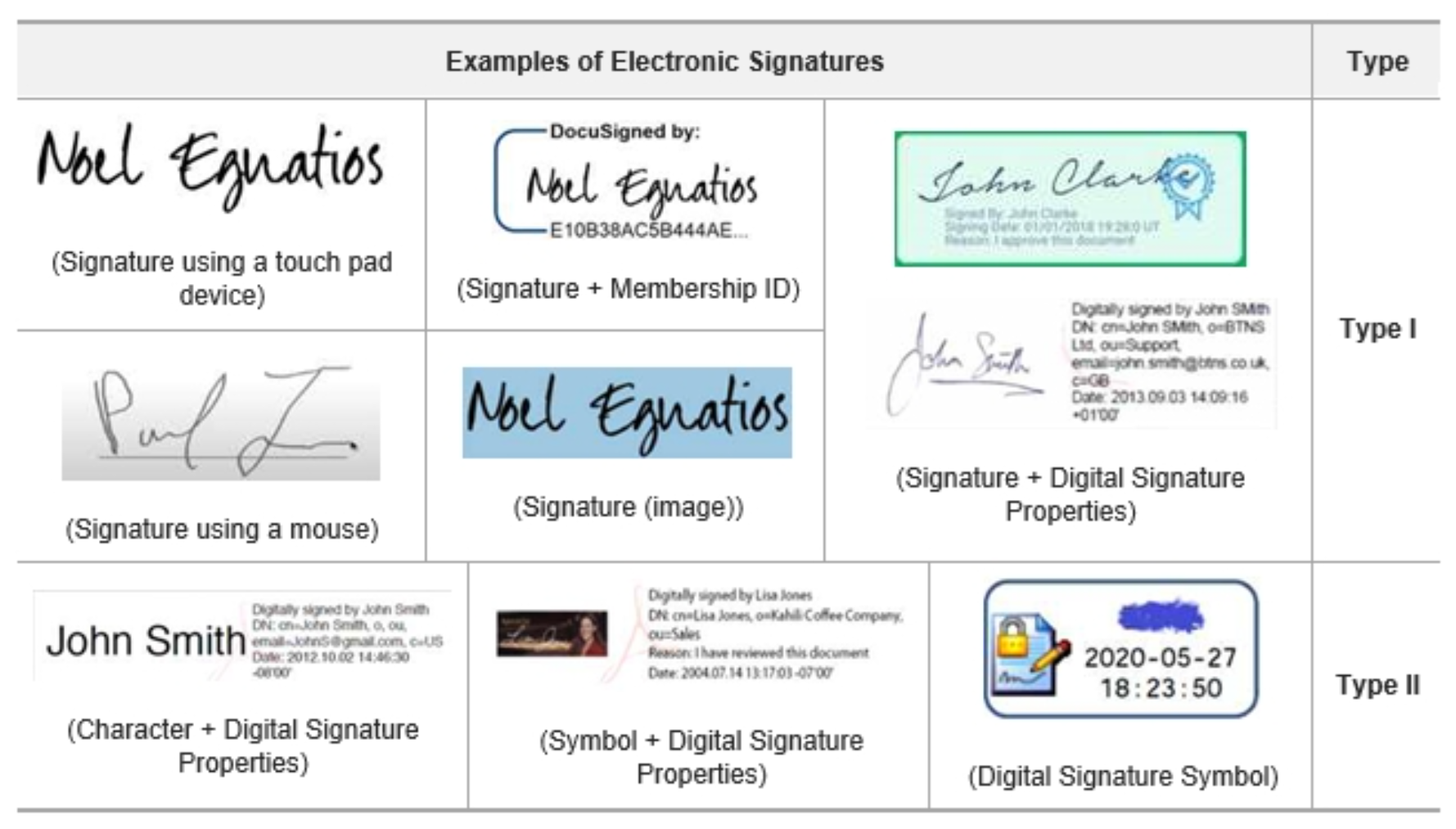
E-Signature

(Context: General, Information Systems Security, Software)
Definition
A digital form of a wet ink signature which is legally binding and secure but it does not incorporate any coding or standards. It can be a symbol, image, process attached to the message or document to recognize the identity and to give consent on it. When we need to only verify the document we use electronic signature.
EA-Solution-Computer-based-Signature-Standard.pdf (virginia.gov)
Early Availability Date
(Context: Technology Management)
Definition
The date by which fully functional hardware or software products are sold for specific user groups for production use as part of an incremental roll-out strategy.
Early availability is typically intended for other hardware or software vendors, who are able to evaluate the new technology in advance of its broader distribution.
Early Finish Date (EF)
(Context: Project Management)
Definition
In the critical path method, the earliest possible point in time on which the uncompleted portions of a schedule activity (or the project) can finish, based on the schedule network logic, the data date, and any schedule constraints. Early finish dates can change as the project progresses and as changes are made to the project management plan.
PMBOK
Early Start Date
(Context: )
Definition
In the critical path method, the earliest possible point in time on which the uncompleted portions of a schedule activity (or the project) can start, based on the schedule network logic, the data date, and any schedule constraints. Early start dates can change as the project progresses, and changes are made to the project management plan.
PMBOK
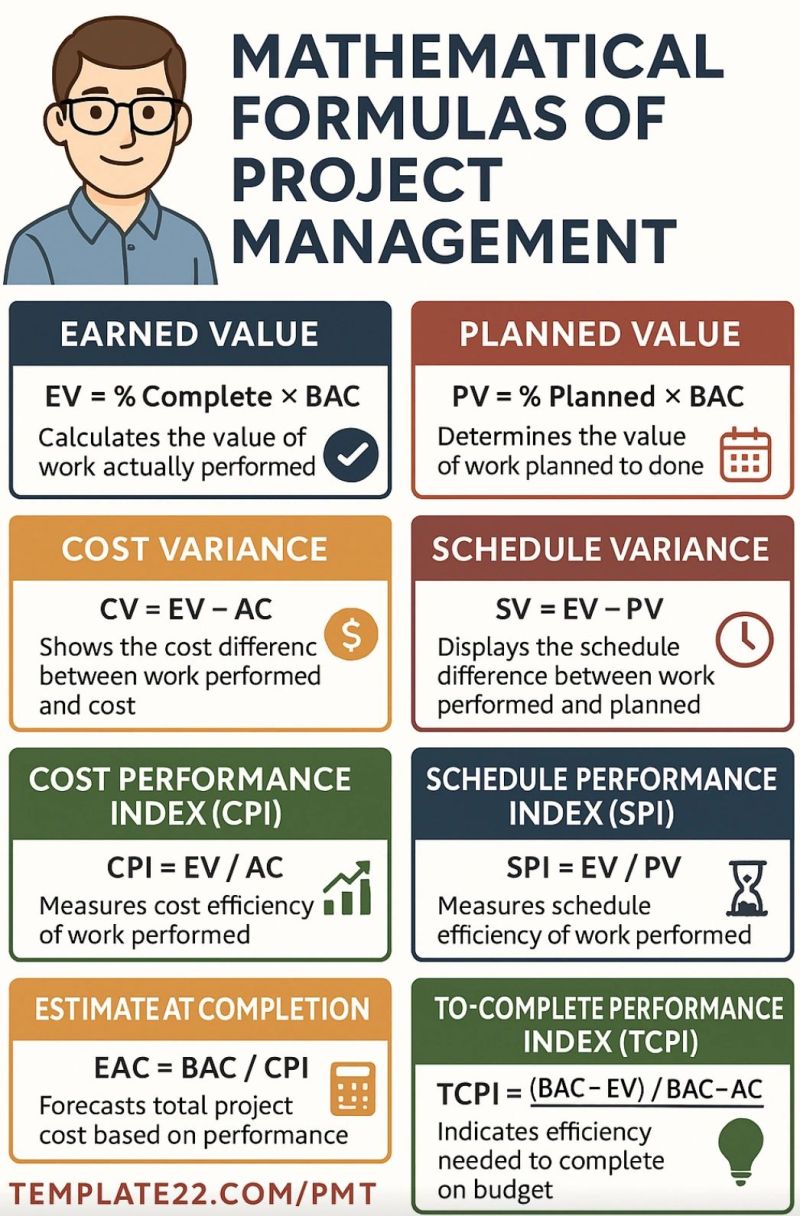
Earned Value (EV)

(Context: Project Management)
Definition
The value of completed work expressed in terms of the approved budget assigned to that work for a schedule activity or work breakdown structure component. Also referred to as the budgeted cost of work performed (BCWP). ProjectManagement.com - What Is The Earned Value (EV) Of A Project | https://www.projectmanagement.com/wikis/711501/what-is-the-earned-value--ev--of-a-project#_
BAC = Budget at Completion
PMBOK
EBCDIC
(Context: )
Definition
Extended Binary Coded Decimal Interchange Code. IBM's 8-bit extension of the 4-bit Binary Coded Decimal encoding of digits 0-9 (0000-1001).
ebXML
(Context: )
Definition
ebXML is a set of specifications that together enable a modular electronic business framework. The vision of ebXML is to enable a global electronic marketplace where enterprises of any size and in any geographical location can meet and conduct business with each other through the exchange of XML based messages. ebXML is a joint initiative of the United Nations (UN/CEFACT) and OASIS, developed with global participation for global usage
Edge Computing
(Context: )
Definition
A distributed computing model that brings computation and data storage closer to the location where it is needed in order to improve response times and save bandwidth.
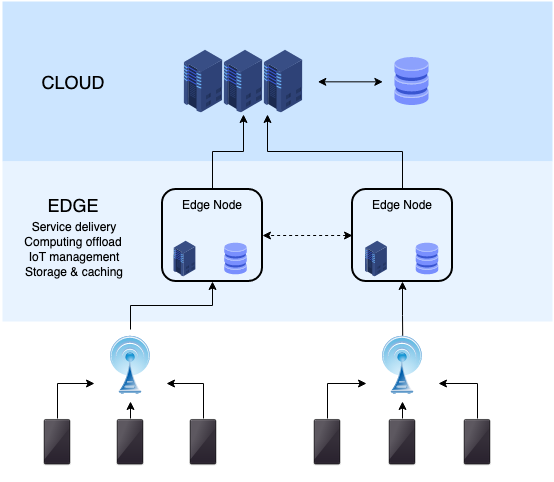
The aim of Edge Computing is to move the computation away from data centers towards the edge of the network, exploiting smart objects, mobile phones or network gateways to perform tasks and interact with cloud-based applications or services. By moving services to the edge, it is possible to provide content caching, service delivery, storage and IoT management resulting in better response times and transfer rates.
EDI
(Context: Software)
Definition
Electronic Data Interchange. EDI works by providing a collection of standard message formats and element dictionary that can be used by businesses to exchange electronically. EDI is used for electronic commerce. EDI interchanges use some variation of the ANSI X12 standard (USA) or EDIFACT (UN sponsored global standard).
What is EDI: Electronic Data Interchange Explained | https://www.comparatio.com/blog/electronic-data-interchange/
Effort
(Context: )
Definition
The number of labor units required to complete a schedule activity or work breakdown structure component. Usually expressed as staff hours, staff days, or staff weeks. Should not be confused with duration.
Electronic Government Virginia (eVA)

(Context: )
Definition
The name for the procurement system used in Virginia government.

Electronic Health Record (EHR)

(Context: General)
Definition
An electronic record of health-related information on an individual that conforms to nationally recognized interoperability standards and that can be created, gathered, managed and consulted by authorized clinicians and staff across more than one health care organization
Electronic Industries Alliance (EIA)
(Context: )
Definition
The Electronic Industries Alliance (EIA) is a non-profit organization that functions as an association of other organizations, one of which is TIA, EIA’s communications arm. The EIA is certified by ANSI to develop standards. The EIA is well known for having produced certain electrical wiring and data transmission standards. Standards are just one part of the organization’s mission, however. The EIA often jointly recommends standards with the Telecommunications Industry Association (TIA). An example standard put forth by both groups is EIA/TIA-232 (also known as EIA-232 and RS-232). This standard establishes how two devices communicate—for example, via the 9 and 25 pin connectors still commonly used on PCs along with USB connectors.
Electronic Information
(Context: )
Definition
Any information stored in a format that enables it to be read, processed, manipulated, or transmitted by an information system.
Electronic Medical Record (EMR)
(Context: )
Definition
An electronic record of health-related information on an individual that can be created, gathered, managed and consulted by authorized clinicians and staff within one health care organization.
Eligible Employees
(Context: )
Definition
Classified, appointed, and hourly employees of the Commonwealth as well as Commonwealth vendors, contractors, and consultants.
Employee to government (E2G)
(Context: )
Definition
Refers to a business process involving electronic interaction of citizens with government.
Encryption
(Context: Information Systems Security)
Definition
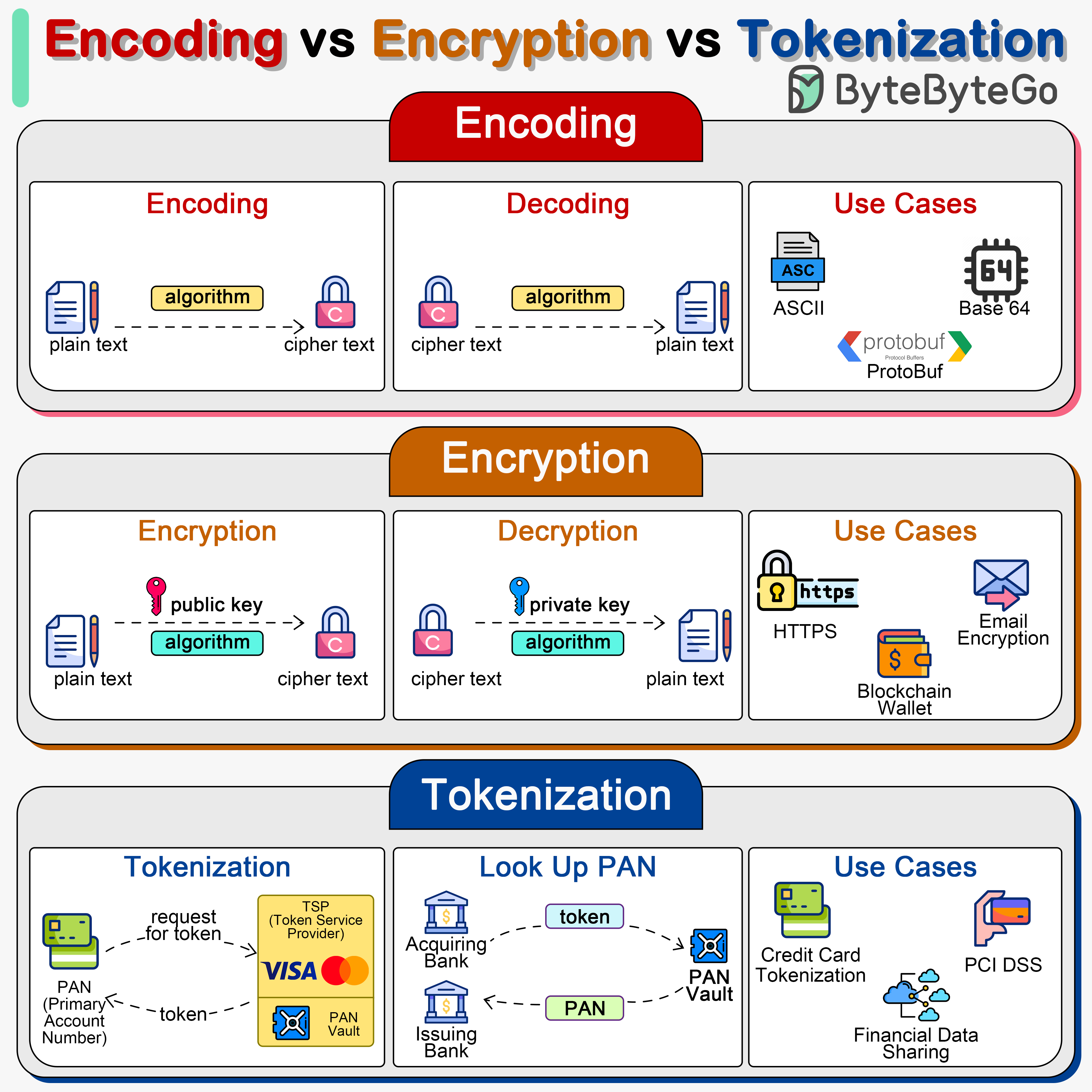
ByteByteGo | Encoding vs Encryption vs Tokenization | https://bytebytego.com/guides/encoding-vs-encryption-vs-tokenization/
The process or the means of converting original data to an unintelligible form so it cannot be read by unauthorized users.
End of Availability Date (EOAD)
(Context: )
Definition
The last date on which a hardware or software product will be sold. In some cases, parts and new security patching support may be available.
End of Extended for Fee Support Date (EEFSD)
(Context: )
Definition
The last date on which a hardware or software product is under vendor or 3rd party support, including security patches, for an additional fee.
End of Life Date (EOLD)
(Context: )
Definition
The last date on which a hardware or software product will have new security patches available.
End of Service Life Date (EOSLD)
(Context: )
Definition
The last date on which a hardware or software product is covered by vendor support, or has vendor supplied parts available, but which still has new security patching support.
End-User
(Context: )
Definition
The final or ultimate user of a computer system. The end-user is the individual who uses the product after it has been fully developed and marketed. The term is useful because it distinguishes two classes of users, users who require a bug-free and finished product (end users), and users who may use the same product for development purposes.
Copyright 2010 Internet.com. All rights reserved. Reprinted with permission from http://www.internet.com.
Engineer
(Context: )
Definition
The Engineer role includes End Users who include, but are not limited to: Developers, Programmers, Database Administrators, Computer Aided Design (CAD) Engineers, or Geographic Information System (GIS) Engineers. These End Users need a performance driven device that supports heavy application driven use cases.
Enhanced Specialized Mobile Radio (ESMR)
(Context: )
Definition
A wireless communication system in which numerous mobile/portable transceivers are linked in a network of repeaters. Each repeater has a range of approximately 5 to 10 miles. Operating frequencies are in the UHF (ultra-high frequency) range, that is, between approximately 300 MHz and 3 GHz. Usually, the working band is near 900 MHz. ESMR can function like its fundamentally simpler cousin, SMR, but it can also offer features similar to those of a cellular telephone network. The PTT (push-to-talk), half-duplex mode can be used; in this case the operation resembles communications between old-style two-way radios. Full-duplex mode can also be used, so either party can listen and talk at the same time. Interconnection with telephone networks is commonly done. In addition to voice communication, an ESMR system can offer paging, wireless fax, and data transmission. ESMR systems use digital radio transmission. Spread-spectrum modes, such as frequency hopping, are common. In a well-designed ESMR system, connection is almost instantaneous, compared with the typical 15 to 20 seconds required to dial and set up a call in a public cellular network. The coverage of an ESMR system depends on the geographical distribution and needs of the users. Some systems are confined to single municipalities; others cover selected groups of metro areas; others operate over entire states or regions of a country. Examples of ESMR networks include Ericsson's EDACS (Enhanced Digital Access Communications System), Motorola's IDEN (Integrated Dispatch Enhanced Network), and the Sprint Nextel System.
Adapted from Whatis.com
Enterprise
(Context: General, Technology Management)
Definition
An organization with common or unifying business interests. An enterprise may be defined at the Commonwealth level, the Secretariat level, or agency level for programs and projects requiring either vertical or horizontal integration within the Commonwealth, a Secretariat, or agency, or between multiple Secretariats, agencies and/or localities.
Technology Business Strategies - Commonwealth Technology Business Plan
Enterprise Application
(Context: Enterprise Architecture)
Definition
Enterprise Applications are provided or sourced to multiple agencies as part of a service. Within the COV enterprise these services are provided by:- COV Agencies (Cardinal by DOA or eVA by DGS, for example)
- VITA CSRM COV Ramp (any application sourced through VITA’s COV Ramp security service)
- VITA CSRM Security Products and Services (Acunetix, Axonius, KnowBe4, etc.)
- VITA Enterprise and Cloud Solutions (Enterprise Service Bus, Large File Transfer, Power Platform, etc.)
- VITA Infrastructure Services MSI or Suppliers (MS Teams, Keystone Edge, Windows Server Virtual Machines, etc.)
Enterprise Application Integration (EAI)
(Context: )
Definition
The use of technology to integrate the application programs, databases, and legacy systems involved in an organization's critical business processes.
Enterprise Architecture (EA)
(Context: )
Definition
A method or framework for developing, implementing, and revising business-focused Information Technology (IT) guidance. The resulting guidance describes how the enterprise can best use technology and proven practices to improve the way it does business. In the Commonwealth, EA is built on the business needs of state and local government agencies. EA is described in a series of documents that showcase the development and revision process, the involved parties, and the resulting guidance. The Commonwealth EA relies on a governance model (roles and responsibilities), business and technical inputs, and knowledge of how agencies presently do business to develop explicit policies, standards, and guidelines for information technology use.
Enterprise Architecture Division
(Context: )
Definition
A division within VITA; the publisher of all VITA external and internal policies, standards, and guidelines. The division develops architectural standards and the accompanying policies and procedures for the enterprise and advises the CIO on architectural standards and exceptions. It also tracks emerging trends and best practices across the spectrum of technologies, including hardware, operating systems, networking and communications, security, and software applications.
Enterprise Business Architecture (EBA)
(Context: Enterprise Architecture)
Definition
The EBA documents the business strategy, governance, organization and business functions of Virginia state government, and identifies which organizations perform those functions. The EBA provides a look at the big picture of state government from a business perspective to define who we are, what we do and where we want to go.
Enterprise Information Architecture (EIA)
(Context: Enterprise Architecture)
Definition
Government and government services are normally information driven. Government organizations constantly and dynamically gather and process data to create information needed to support their missions, whether it is disaster recovery, environmental protection, citizen security or other direct services. The Enterprise Information Architecture (EIA) provides the framework/model and methodology that will enhance each agency’s ability to quickly discover, access and understand data and create the information needed to make critical decisions and support agency business functions.
The EIA is designed to provide a common framework for the cost-effective sharing of government information across organizational lines while respecting the security, privacy and appropriate use of that information. It must enable agency leaders to manage information as a Commonwealth asset to better serve the citizens of Virginia. It increases the Commonwealth’s agility in drawing out the value of information as a strategic mission asset.
Enterprise Mobility Management (EMM)
(Context: Technology Management)
Definition
A set of technology, processes, and policies to secure and manage the use of corporate and employee-owned mobile devices within an organization.
https://www.vita.virginia.gov/media/vitavirginiagov/it-governance/ea/pdf/Event-Log-Management.pdf
Enterprise Program Management (EPM)
(Context: )
Definition
An Information Technology Investment Management-based methodology to manage programs and projects of enterprise significance. EPM focuses on the management of multiple related programs and projects that individually support the same mission or ongoing activity.
Enterprise Service
(Context: )
Definition
Reusable Business Services providing standards-based capabilities or functions that solve business problems, and which can be combined with other services to meet new requirements, compose new applications, or enable new Business Processes.
Enterprise Solutions Architecture (ESA)
(Context: Enterprise Architecture)
Definition
The expectations of government to deliver more services, to deliver them better and more cheaply presents a challenge for the Commonwealth. Well-engineered automated solutions1 can increase productivity in service delivery to help meet these expectations.
Commonwealth agencies make significant investments in these automated solutions in order to carry out the business of Virginia government.2 The Commonwealth Enterprise Solutions Architecture (ESA) provides the framework/model and methodology that supports the transition from silo-based, application-centric and agency-centric information technology investments to an enterprise approach where solutions are designed to be flexible. This allows agencies to take advantage of shared and reusable components, facilitates the sharing and reuse of data where appropriate and makes the best use of the technology infrastructure that is available.
The ESA needs to contain a unified view of solutions to achieve this increase in reuse and the reduction of solution complexity. To support this, the framework/model and methodology includes: inventories, governance/guidance and the relationships between agency applications and the other EA component architectures.
Enterprise Technical Architecture (ETA)
(Context: Enterprise Architecture)
Definition
The ETA guides the development and support of an organization’s information systems and technology infrastructure.
Enterprise Technology Program
(Context: )
Definition
A group of related IT projects, aggregated for management purposes that support a defined enterprise. Enterprise-wide technical architecture (EWTA) Enterprise-wide technical architecture.
Enterprise-wide technical architecture
(Context: )
Definition
Design and structure of an organization’s information technology (IT) systems and infrastructure. It encompasses the frameworks, standards, technologies, and principles that guide the development, integration, and management of IT systems across the entire enterprise.
Entity
(Context: )
Definition
A person, place, thing, event or concept identified by a user or an agency as having an independent existence and capable of being uniquely identified (e.g. Customer, Vendor, and Address).
Entity Relationship Diagram (ERD)
(Context: )
Definition
An abstract representation of structured data, which produces a conceptual data model of a system and its requirements. The actual model is frequently called an "Entity-Relationship Model" because it depicts the entities and relationships existing in the data. An ERD (the diagram of the model) may also be referred to as an Entity Relationship Model (ERM) or a Logical Data Model (LDM).
Equivalent
(Context: )
Definition
Content is "equivalent" to other content when both fulfill essentially the same function or purpose upon presentation to the user. In the context of this document, the equivalent must fulfill essentially the same function for the person with a disability (in as feasible a manner as possible given the nature of the disability and the state of technology) as the primary content does for the person without any disability. For example, the text "The Full Moon" might convey the same information as an image of a full moon when presented to users. Note that equivalent information focuses on fulfilling the same function. If the image is part of a link and understanding the image is crucial to choosing the link target, an equivalent must also give users an idea of the link target.
ERwin
(Context: )
Definition
A database design and optimization tool from Computer Associates.
Essential Business Function
(Context: )
Definition
A business function is essential if disruption or degradation of the function prevents the agency from performing its mission as described in the agency mission statement.
Estimate
(Context: )
Definition
A quantitative assessment of the likely amount or outcome. Usually applied to project costs, resources, effort, and duration and is usually preceded by a modifier (i.e.,) preliminary, conceptual, feasibility, order of-magnitude, definitive). It should always include some indication of accuracy (e.g. + percent).
PMBOK
Estimate at Completion (EAC)
(Context: )
Definition
The expected total cost of a schedule activity, a work breakdown structure component, or the project when the defined scope of work will be completed. EAC is equal to the actual cost (AC) plus the estimate to complete (ETC) for all of the remaining work. EAC=AC plus ETC. The EAC may be calculated based on performance to date or estimated by the project team based on other factors, in which case it is often referred to as the latest revised estimate.
PMBOK
Estimate to Complete (ETC)
(Context: )
Definition
The expected cost needed to complete all the remaining work for a schedule activity, work breakdown structure component, or the project.
PMBOK
Ethernet
(Context: )
Definition
A local-area network (LAN) protocol that is specified in IEEE 802.3 and that uses CSMA-CD to provide 10 Mbps service over copper. Switched Ethernet provides faster service (e.g., 100 Mbps Ethernet, 10GigE). Gigabit (GB) and 10 GB Ethernet service are now possible. GB Ethernet is used mainly for backbone services and wide area networking.
Ethics
(Context: )
Definition
In the conduct of their operations, state organizations and their employees will employ information technology in a legal and ethical manner consistent with government statutes, rules, and regulations. Information technology will not be used for purposes that are unrelated to the state organization's mission or violates state or federal law. Contract provisions, including software licensing agreements, will be strictly enforced.
Evaluation
(Context: )
Definition
Procedures used in the analysis of security mechanisms to determine their effectiveness and to support or refute specific system weaknesses.
Event
(Context: )
Definition
An , including failures of service delivery, security breaches.
Event Log Forwarding
(Context: Technology Management)
Definition
A service that allows network administrators to forward events from multiple servers and collect them in one location.
https://www.vita.virginia.gov/media/vitavirginiagov/it-governance/ea/pdf/Event-Log-Management.pdf
Everything over IP (EoIP)
(Context: )
Definition
Everything over IP.
Exception Report
(Context: )
Definition
Document that includes only major variations from the plan.
PMBOK
Expected Monetary Value Analysis
(Context: )
Definition
A statistical technique that calculates the average outcome when the future includes scenarios that may or may not happen. A common use of this technique is within decision tree analysis. Modeling and simulation are recommended for cost and schedule risk analysis because it is more powerful and less subject to misapplication than expected monetary value analysis.
PMBOK
Extended SMTP (ESMTP)
(Context: )
Definition
Initially defined in RFC 1869 and extended thereafter.
Extensible
(Context: )
Definition
Quality of a system that allows new features and functions to be added to it.
Extensible Markup Language (XML)
(Context: )
Definition
XML is a simple, very flexible text format derived from SGML (ISO 8879). Originally designed to meet the challenges of large-scale electronic publishing, XML is also playing an increasingly important role in the exchange of a wide variety of data on the Web and elsewhere.
Extensible Markup Language (XML) Schema
(Context: )
Definition
XML Schemas express shared vocabularies and allow machines to carry out rules made by people. They provide a means for defining the structure, content and semantics of XML documents.
Extensible Stylesheet Language (XSL)
(Context: )
Definition
XSL is a family of recommendations for defining XML document transformation and presentation. It consists of three parts:
- XSL Transformations (XSLT)-a language for transforming XML
- The XML Path Language (XPath)-an expression language used by XSLT (and many other languages) to access or refer to parts of an XML document
- XSL Formatting Objects (XSL-FO)- an XML vocabulary for specifying formatting semantics.
External Information System
(Context: )
Definition
An information system designed and intended for use by external agency customers and/or by the public. COV employees, contractors, and business partners may also use such systems. See also Information System and Internal Information System.
External Standard
(Context: Commonwealth Data Management Program)
Definition
A standard defined and maintained by a Standards Development Organization to improve the ability to share electronic data and ensure semantic interoperability. Generally may apply to services, documents, vocabularies (i.e., reference terminologies) and/or messages. Includes extending (e.g., adding data elements or codes to) an existing external standard to accommodate requirements specific to the Commonwealth.
Extranet
(Context: )
Definition
A web site or web site area created for use by a select group. The group is usually the company's employees, clients, and/or select members of the public. An extranet allows for secure exchange of information within the select group - generally about a particular topic. It can also contain forms and applications relevant to the group's needs. For purposes of determining if a website, website area, or application must comply with the Web Site Standard, an "extranet" refers to any online area where access is restricted to a select group of users (by IP address, authentication, VPN, or other technical means). Note that all online material (even extranets and intranets) must comply with the Accessibility Standard.
